Rice is a staple food for billions worldwide and has a rich history spanning thousands of years. Across various cultures and regions, numerous varieties of rice have been cultivated, each with its unique characteristics and significance.
Join us on a journey through time as we delve into ancient grains, uncover the 10 oldest rice varieties, and explore their origins, years of cultivation, and intriguing facts.
11. Wehani Rice
Year of Cultivation: 20th Century AD
Country of Origin: United States

Wehani Rice was developed in the late 20th century in the United States. It is a hybrid variety known for its reddish-brown color and aromatic fragrance. With origins in California, this rice has gained popularity for its nutty flavor and versatility in various culinary applications.
Did You Know?
Wehani Rice was created through traditional cross-breeding methods to combine aromatic Basmati rice with long-grain American rice varieties.
10. Senia Rice
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 20th Century AD
Country of Origin: Spain
Senia Rice originated in the early 20th century in the Valencia region of Spain. It is a medium-grain rice known for absorbing flavors while retaining a firm texture. This versatile rice is commonly used in Spanish paella and other Mediterranean dishes.
Did You Know?
Senia Rice is favored by chefs for its ability to absorb flavors without becoming overly sticky, making it ideal for various culinary creations.
9. Basmati Rice
Year of Cultivation: India and Pakistan
Country of Origin: Ancient times

Basmati rice is renowned for its distinctive aroma and long, slender grains. It traces its origins to the Indian subcontinent. This aromatic rice variety has been cultivated for centuries along the foothills of the Himalayas. Known for its exceptional fragrance and delicate flavor, Basmati rice remains a culinary delight and an integral part of Indian and Pakistani cuisine.
Did You Know?
Basmati rice is often aged to enhance its flavor and aroma, making it a sought-after choice for gourmet dishes and traditional meals.
8. Arborio Rice
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 14th Century AD
Country of Origin: Italy

Arborio Rice originated in the Po Valley of Italy around the 14th century AD. It is well-known for its high starch content, which results in a creamy texture when cooked. This short-grain rice is a staple in Italian cuisine, particularly risotto dishes.
Did You Know?
The unique starch composition of Arborio Rice allows it to release starch slowly, giving risotto its characteristic creamy consistency.
7. Thai Jasmine Rice
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 12th Century AD
Country of Origin: Thailand

Thai Jasmine Rice has been cultivated in Thailand since the 12th century AD. It is prized for its delicate floral aroma and soft, slightly sticky texture when cooked. This aromatic variety has gained international acclaim for its fragrance and taste.
Did You Know?
Thai Jasmine Rice is often used in Southeast Asian cuisine and is a preferred choice for dishes like Thai curries and stir-fries due to its fragrance and ability to absorb flavors.
6. Bhutanese Red Rice
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 800 AD
Country of Origin: Bhutan

Bhutanese Red Rice has been cultivated in the Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan since approximately 800 AD. With its reddish-brown bran layer, this heirloom variety adds a distinct nutty taste to traditional Bhutanese cuisine.
Did You Know?
Bhutanese Red Rice is organically grown in terraced fields in the pristine mountainous landscapes of Bhutan and is a staple in the country’s diet.
5. Red Camargue Rice
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 500 BC
Country of Origin: France
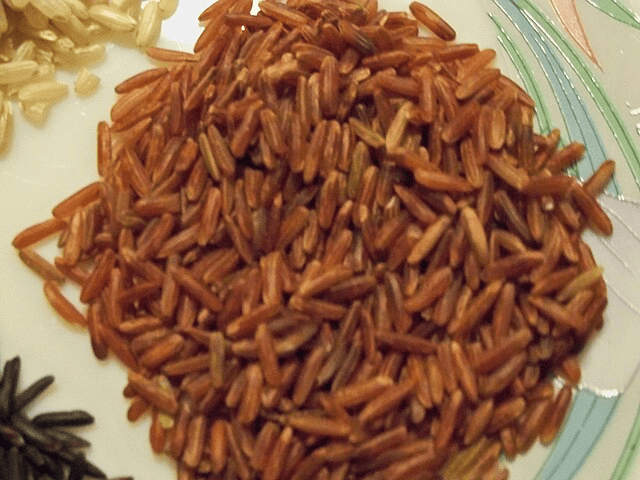

Red Camargue Rice was cultivated in the Camargue region of France since around 500 BC. It is known for its distinctive red husk and nutty flavor. This heirloom variety thrives in the unique ecosystem of the Rhône River delta.
Did You Know?
Red Camargue Rice gains its reddish hue from its outer layer, which contains anthocyanins, natural antioxidants believed to offer health benefits.
4. Chinese Black Rice (Forbidden Rice)
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 500 BC
Country of Origin: China

Chinese Black Rice, often referred to as Forbidden Rice, has a history dating back to around 500 BC in China. Initially reserved for Chinese royalty due to its rarity, this dark-hued rice is celebrated for its nutty flavor and nutritional richness.
Did You Know?
Forbidden Rice gets its name from ancient China, where it was considered so precious and nutritious that commoners were forbidden from consuming it.
3. Oryza Glaberrima (African Rice)
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 1500 BC
Country of Origin: West Africa

African Rice, scientifically called Oryza Glaberrima, has a history dating back to around 1500 BC in West Africa. This indigenous rice species has adapted to local climates and is a significant part of West African culinary traditions.
Did You Know?
African Rice played a crucial role in sustaining ancient African civilizations and continues to be cultivated in regions like Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Senegal.
2. Oryza Sativa Japonica (Japanese Rice)
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 2400 BC
Country of Origin: Japan
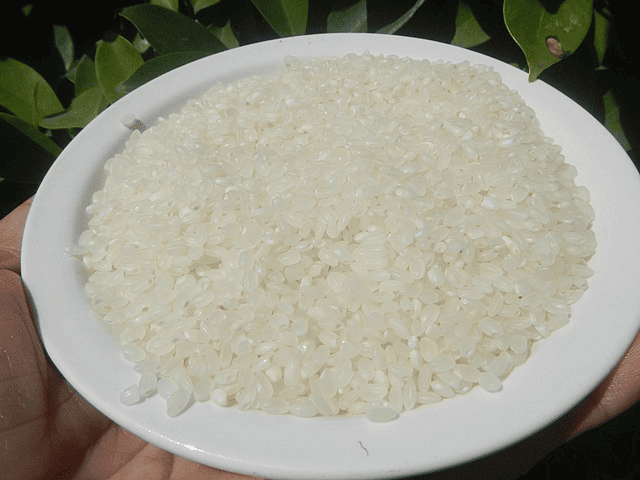

Japanese Rice, known scientifically as Oryza Sativa Japonica, boasts a long history dating back to around 2400 BC. Renowned for its sticky texture and suitability for sushi and other traditional Japanese dishes, this variety continues to be a cornerstone of Japanese cuisine.
Did You Know?
Japanese Rice is highly prized for its distinct taste and ability to absorb flavors, making it an integral part of the gastronomic culture in Japan.
1. Oryza Sativa Indica (Indian Rice)
Year of Cultivation: Approx. 5000 BC
Country of Origin: India
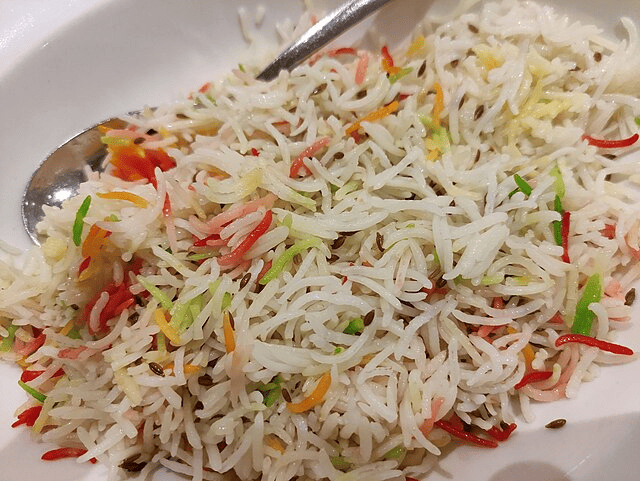

Indica rice, scientifically classified as Oryza Sativa Indica, traces its roots to around 5000 BC in India. Known for its long-grain structure and aromatic qualities, Indian Rice varieties like Basmati and Jasmine are cherished in global cuisine.
Did You Know?
Basmati rice, a type of Indian Rice, is famed for its delicate aroma and is often considered one of the finest rice varieties globally.
Conclusion
The diverse array of ancient rice varieties showcases this staple grain’s rich cultural heritage and culinary significance. From Asia to Europe, these oldest rice varieties have shaped regional cuisines, offering unique flavors, textures, and historical tales that continue to enrich culinary traditions around the globe.