The earliest human-like species or hominid appeared for the first time around about 2 million years ago. Early homo sapiens or modern humans appeared in Africa around 20,000 years ago.
After thousands of years, these homo sapiens laid the foundation for the early forms of human civilizations with the development of agriculture, weaponry, art, social structure, and politics.
Although Mesopotamia is typically considered as the first urban civilization, several complex societies and cultures were practiced way before that. These can be considered as civilizations and hence are included in the list.
So, history geeks assemble, we present the 10 oldest civilizations in the world.
Top 10 Oldest Civilizations in the World
10. Akkadian Empire
Era: c.2350 BCE – 2150 BCE
Location: Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia (modern-day Iraq, Syria, and Turkey)
Notable Achievements: One of the world’s first empires
Still Around: No
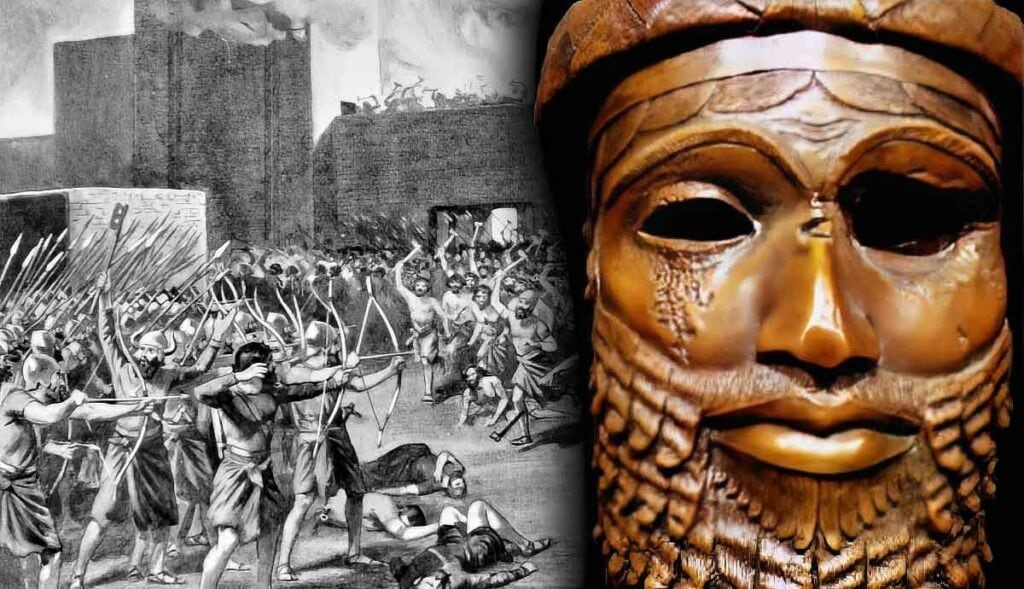 photo source: The Collector
photo source: The Collector
Since the empire combined two distinct yet similar civilizations, its people were bilingual, speaking both Sumerian and Akkadian and writing in the Akkadian version of Cuneiform.
The Akkadians regularly traded with the nearby Indus Valley Civilization. The Sumerians and Akkadians had a surplus of agricultural products, which they traded for metal ores, timber, and building stone.
The people of the Akkadian Empire were skilled craftsmen and made a number of beautifully carved seals and cast metal statues.
Did You Know?
The fall of the Akkadian Empire gave rise to two famous empires, Assyria in the north and Babylon in the south.
9. Ancient Egyptians (c. 3,150 BCE – 332 BCE)
Era: c.3100 BCE – 30 BCE
Location: Nile River Valley of Egypt
Notable Achievements: The Great Pyramids
Still Around: No
Ancient Egyptian civilization is traditionally stated to have started around 3,150 BCE when King Menes unified Upper and Lower Egypt and established a capital city at White Walls (later called Memphis). Egyptians are perhaps the most well known of the ancient civilizations.
While they made several social, cultural, and political advancements, ancient Egyptian civilization is best known for creating The Great Pyramids in Ancient Egypt era, which still remains as one of the great wonders of the world. The ancient Egyptians developed construction techniques that enabled them to build massive monuments such as pyramids, temples, and obelisks.
Some of their other achievements include creating a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems, the first known planked boats, glass technology, and new forms of literature.
Many things we use today were first invented by the ancient Egyptians such as mints, paper, door locks, alarm clocks, concrete, and much more.
Did You Know?
While the beautiful hieroglyphics of the Ancient Egyptians are largely associated with the civilization, it was not actually the common writing system. Hieroglyphics were used only in special circumstances and scribes used hieratic and later, demotic (both were simplified versions of hieroglyphics).
8. Indus Valley Civilization
Era: c.3300 BCE – 1300 BCE
Location: South Asia (modern-day Pakistan and northwest India)
Notable Achievements: One of the first systems of uniform weights and measures and urban
Still Around: No
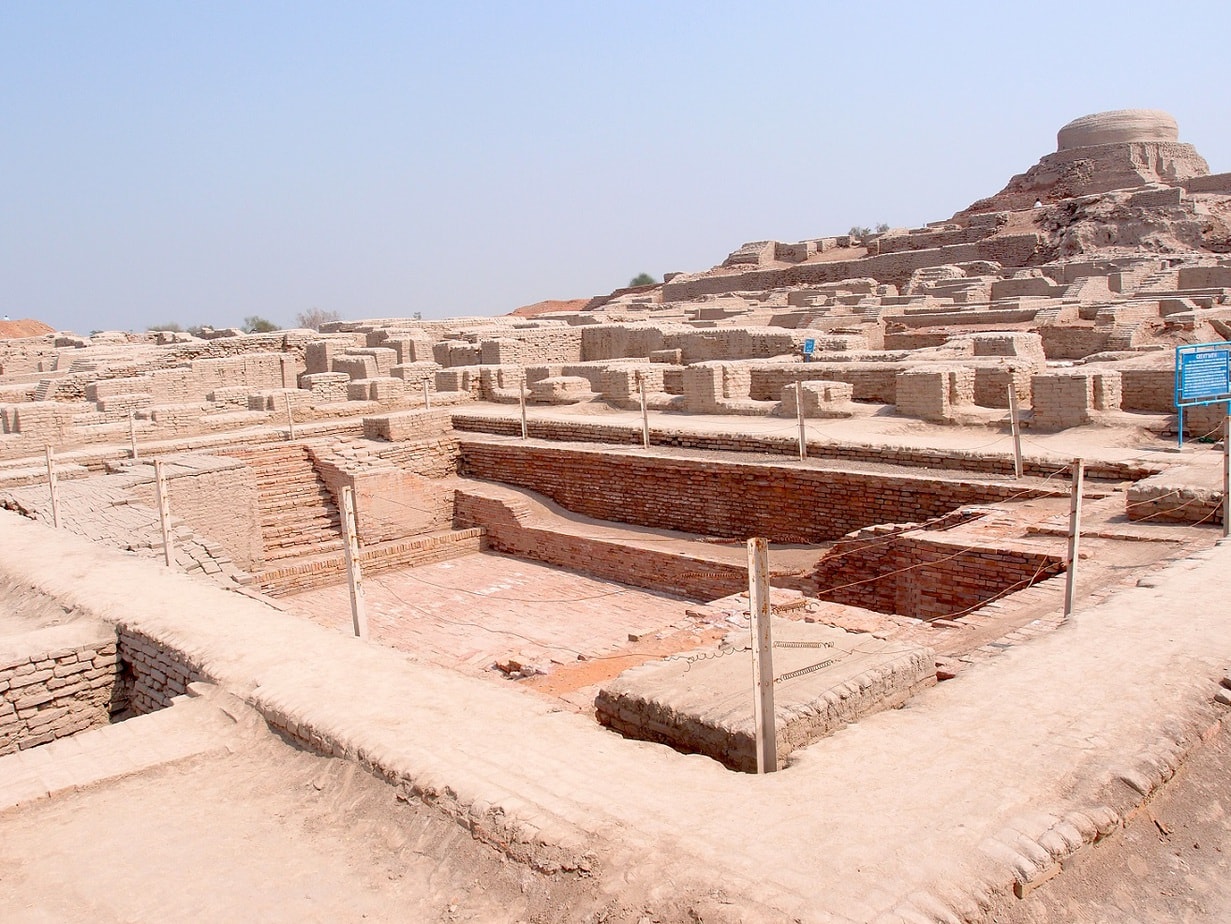 photo source: Wikimedia Commons via Saqib Qayyum
photo source: Wikimedia Commons via Saqib Qayyum
The Indus Valley Civilization or Harappan Civilization was the first urban civilization in South Asia (modern-day Pakistan and northwest India). The Harappans built numerous sprawling cities, which were notable for their urban planning, water supply systems, elaborate drainage systems, and large concentrations on non-residential buildings.
The people of the Indus Valley also developed a number of technologies, including one of the world’s first systems of uniform weights and measures. They also created new techniques in metallurgy and produced copper, bronze, lead, and tin.
In addition to math and engineering, the Indus Valley Civilization enjoyed a number of arts and crafts. Various games and toys have also been found in Indus Valley Civilization cities.
Did You Know?
For such a large and successful civilization, there is no evidence that the Indus Valley Civilization was ruled over by a King or some other singular ruler. Instead, the Indus Valley Civilization was most likely ruled by a central government, which would explain the extensive city planning.
7. Norte Chico
Era: c.3500 BCE – 1700 BCE
Location: Peru
Notable Achievements: Monumental architecture including sunken circular plazas and earthwork platform mounds
Still Around: No
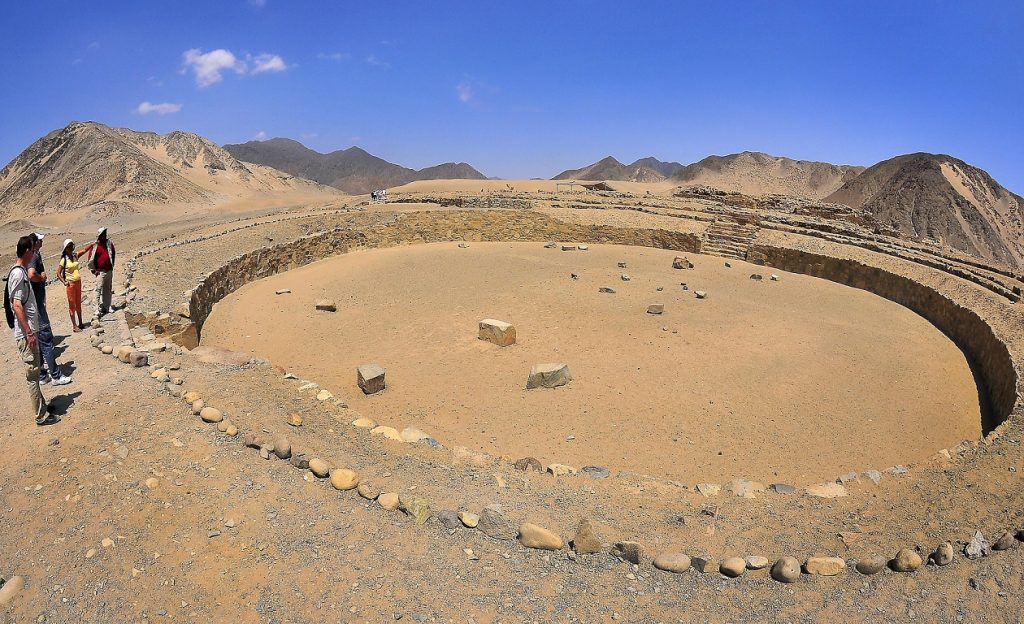 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
The Norte Chico civilization (also called Caral or Caral-supe civilization) is considered to be the oldest known civilization that existed in the Americas. The formation of the civilization’s first city happened around 3,500 BCE and from this time until a period of decline around 1,800 BCE, the Norte Chico people flourished.
The Norte Chico civilization is a pre-ceramic ancient culture as archaeologists have found no ceramic remains and almost no visual art. However, the Norte Chico people are known for their monumental architecture which includes large earthwork platform mounds and sunken circular plazas (such as the one pictured above).
Did You Know?
In Caral, the city for which the Norte Chico civilization gets its other name, a total of six pyramids have been discovered – they are the oldest pyramids outside of Egypt and are actually contemporary with the first Egyptian pyramids.
6. Mesopotamia (c. 6,500 BCE – 539 BCE)
Era: c.8000 BCE – 2000 BCE
Location: Ancient Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq)
Notable Achievements: Invention of the wheel
Still Around: No
 photo source:Wikimedia Commons
photo source:Wikimedia Commons
Around 10,000 BCE, some of the first fully developed Neolithic cultures began to settle in the fertile crescent, which includes Mesopotamia. Around 8,000 BCE, people in northern Mesopotamia began to cultivate barley and wheat, which they used to make beer, gruel, soup, and eventually bread.
During the time known as the Ubaid Period (c. 5,500 BCE – 4,000 BCE), the earliest signs of civilization began as agriculture and animal husbandry were widely practiced in sedentary communities. This gave rise to the Sumerians, who are credited as the first urban civilization in the world.
The Sumerians were the first to develop trade and establish industries such as weaving, leatherwork, metalwork, masonry, and pottery. One of the greatest achievements of ancient Mesopotamia was the invention of the wheel some time around 3,500 BCE – evidence suggests that they were first used for making pottery and not for transportation.
Did You Know?
The Sumerians also developed the world’s first writing system, Cuneiform, around 3200 BCE. Cuneiform also influenced many other early writing systems.
5. Jiahu (c. 7,000 BCE – 5,700 BCE)
Era: c.7000 BCE – 5700 BCE
Location: Henan, China
Notable Achievements: Jiahu symbols one of the earliest examples of writing and some of the oldest playable instruments
Still Around: No
 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
Jiahu was a settlement located in the central plain of ancient China and the people who lived there developed some of the earliest aspects of Chinese culture and Chinese civilization. The Jiahu culture is often mentioned with the Peiligang culture, as archaeologists cannot agree whether or not the Jiahu people were a part of the larger group of Peiligang.
However, there is evidence that they were two separate cultures that developed around the same time. For example, the people of Jiahu cultivated rice while the Peiligang did not and the Jiahu settlement existed for several hundred years before the first Peiligang settlements popped up.
The Jiahu are also known for producing the world’s oldest wine, some of the earliest playable music (lots of flutes have been found at Jiahu), and perhaps the earliest example of Chinese writing.
The Jiahu symbols are 16 distinct markings found on prehistoric artifacts and are believed to have been indicative of sign usage rather than systematic writing.
Did You Know?
Archaeological evidence suggests that Jiahu was abandoned around 5700 BCE due to a massive flood. Since few artifacts have been discovered in the residences at Jiahu, it is believed that the settlement’s residents were able to evacuate with most of their belongings.
4. ‘Ain Ghazal (c. 7,200 BCE – 5,000 BCE)
Era: c.7250 BCE – 5000 BCE
Location: Ayn Ghazal (modern-day Amman, Jordan)
Notable Achievements: ‘Ain Ghazal statues
Still Around: No
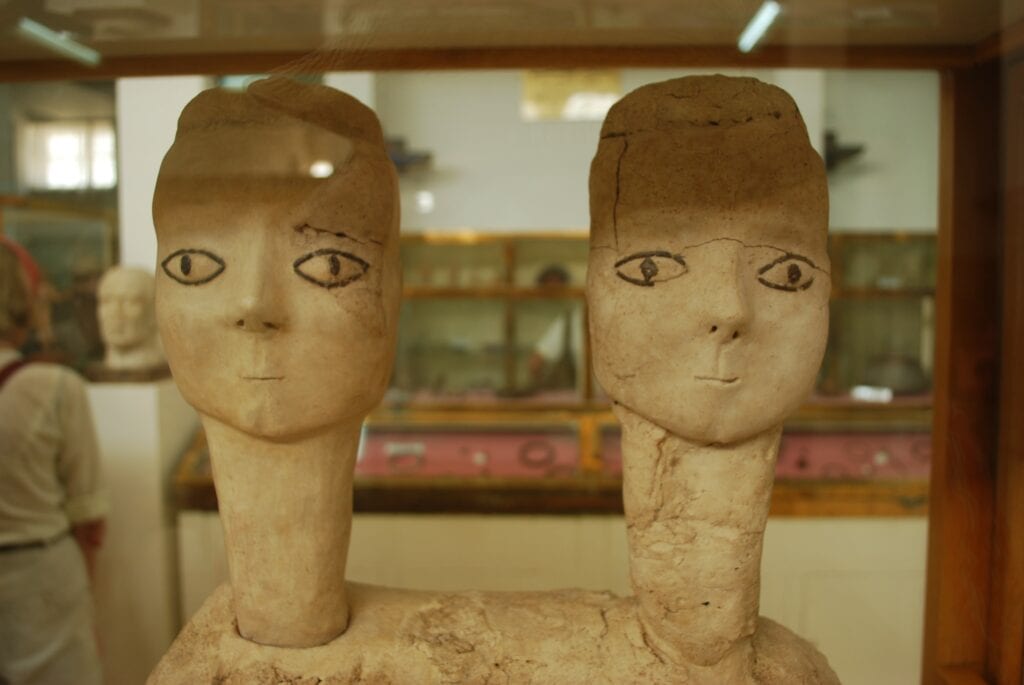 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
In addition to creating the statues, the people of ‘Ain Ghazal were farmers who domesticated wheat, barley, peas, lentils, and chickpeas. They also hunted wild animals such as gazelle, deer, pigs, foxes, and hares. For the time period, the people of ‘Ain Ghazal had eaten a wide variety of food.
Did You Know?
Archaeologists have discovered evidence of social class distinction in ‘Ain Ghazal, such as how only some people, about one every 15-20 years, were buried, while nearly everyone else was disposed of in the garbage.
3. Çatalhöyük (c. 7,500 BCE – 5,700 BCE)
Era: c.7500 BCE – 6400 BCE
Location: Southern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey)
Notable Achievements: One of the earliest urban settlements
Still Around: No
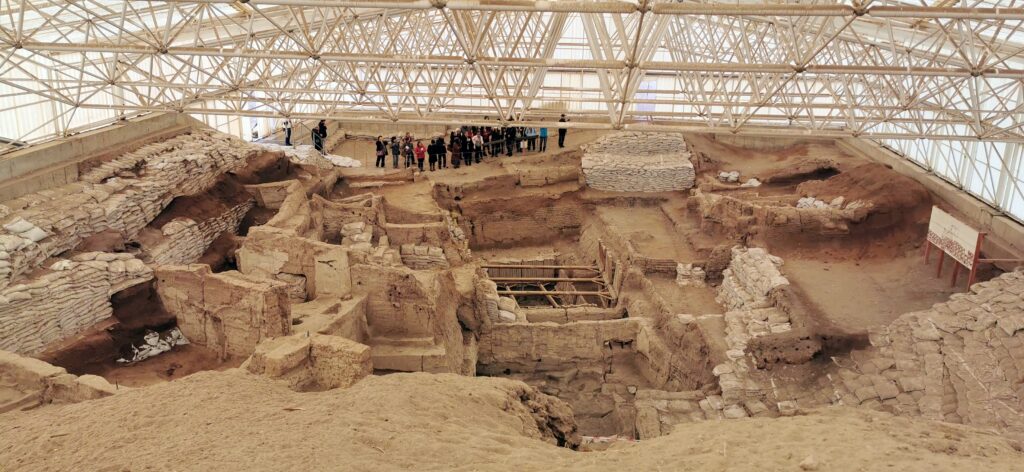 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
The settlement of Çatalhöyük is one of the oldest urban settlements and one of the most well-preserved Neolithic settlements. Excavations of the site have revealed evidence of prehistoric social organization and cultural practices.
The people of Çatalhöyük were one of the earliest people to adapt to a sedentary life and practice agriculture. It is estimated that the average population of Çatalhöyük was between 5,000 – 7,000.
The settlement has no streets or footpaths, instead the houses were clustered together with roof access. There is also evidence that the people of Çatalhöyük kept their living spaces clean and disposed of their sewage and food in an area outside of the ruins of the settlement.
The people of Çatalhöyük also buried their dead, painted murals, sculpted figurines, and even plastered and painted skulls to recreate faces.
Did You Know?
No identifiable temples have been discovered in Çatalhöyük, but researchers believe the settlement’s people had a religion rich in symbols as large concentrations of certain symbols have been found in some rooms, which may have been shrines or meeting places.
2. Aboriginal Australians
Era: c.50,000 years ago – Present
Location: Australia
Notable Achievements: Oldest known ritual cremation, some of the oldest known rock paintings, and built the oldest structures (fish traps)
Still Around: Yes
 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
Although the people who settled in Mesopotamia are often credited as the first civilization, new research shows that Aboriginal Australians are one of the oldest known civilizations on Earth.
The Aborigines can trace their ancestries back to about 75,000 years ago, but became a distinct genetic group around 50,000 years ago.
It is believed that this ancient group of Aboriginal Australians first settled in Australia between 40,000 – 31,000 years ago. They are the direct ancestors of today’s remaining Aboriginal tribes and their culture has largely remained the same.
The discovery of the human remains from Lake Mungo in New South Wales, Australia in 1969 show signs of being one of the oldest known cremations. The remains, which are known as the Mungo Woman, have been dated to about 24,700 – 19, 030 years ago.
Did You Know?
The Aboriginals built one of the world’s oldest known sturctures, the Ngunnhu fish traps of Brewarrina, which are at least 40,000 years old.
1. San People
Era: c.140,000 to 100,000 years ago – present
Location: Southern Africa in countries such as Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, and South Africa
Notable Achievements: Some of the oldest known rock paintings and oldest known ritual ceremony
Still Around: Yes
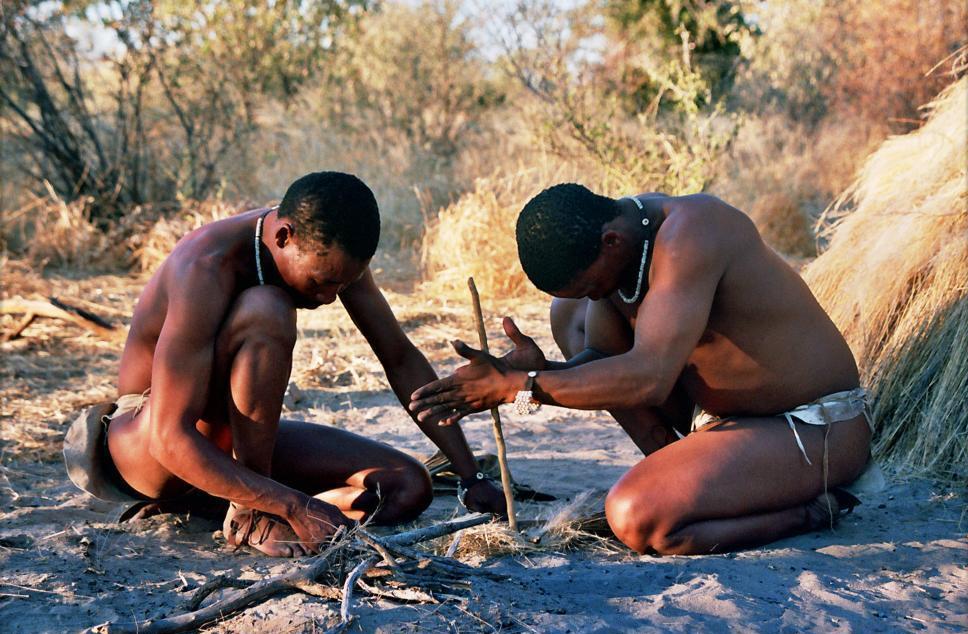 photo source:Wikimedia Commons via Ian Sewell
photo source:Wikimedia Commons via Ian Sewell
The San People of Southern Africa trace their history directly to ancient peoples who lived around 140,000 to 100,000 years ago. In fact, the San are the direct descendants of one of the original ancestral human groups (haplogroup), making the San the oldest civilization in the world.
In the past, the San were semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers, but today many San work as farm laborers, run nature conservancies, and other various small jobs as hunting and gathering alone is no longer sustainable.
Recent archaeological finds have uncovered the oldest known ritual ceremonies, which have been been attributed to the San in the ancient world.
Archaeologists discovered 70,000-year old spearheads in a cave in the Tsodilo Hills of Botswana that were sacrificed to the python. The Tsodilo Hills are also notable for being the site of the world’s largest concentration of rock paintings. This art was also made by ancient San people.
Did You Know?
The San received the world’s first royalty agreement for their traditional knowledge of the Hoodia gordonii, which is currently being developed into a pharmaceutical drug for dieting.
Conclusion
Rise of agriculture and trade which resulted in surplus food and economic stability marked the beginning of civilization. Human history is fascinating. We have come a long way. We have evolved biologically, socially and in many ways, making life easier today.
These 10 oldest civilizations in the world give us a glimpse into lives tens of thousands of years ago. Each of these civilizations has contributed to humanity in one way or another.
So, let me sit in the electrically lit room, typing on a computer and reminiscing about our ancestors!
OTHER POSTS YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN












What about Indus Valley Civilization, which is not only older than many of these civilization but also was more advanced.
They were around from c. 2600 – c. 1900 BCE – so not quite as old
The remains of Indus valley civilisation that have been found are at least 5000 years old, and very much complex and advanced – indicating that the civilisation would have begun much much earlier. They traded basic human needs like food for ornamental items with other civilisations like the Mesopotamians and Chinese, which also indicates their self sufficiency in food and higher states of existences.
It has been found that Mehrgarh in the Indus Valley goes back 12000 years. They could drill teeth and create pots on wheels and sail the sea from the Indus Valley to Sumeria. Sumerians came in from somewhere else and passed through the Indus Valley. The Sumerians had a language related to people in Hungary called the Magyars.
You did not give any details about Aboriginal Australian civilization 40,000 years ago, just a cremation 24,000 years ago. Or does does the ability to migrate to a distant continent imply civilization?
What about danube civilization which is 5500 years old ? Vinca site in Serbia shows that people where living in houses 5ooo bc while the rest of europe were still in stone age, also they invented the wheel before its considered to be in mesopotamia. They found one i slovenia 5000 years old and more. On balkan area you have first metallurgy, in Sibenik in croatia (danilo culture) they found evidence of first milk fermention (cheese making) 7200 years bc. There was a civilization on balkan that no one seem to know about or care what after all this article seems to represent.