Slavic languages are a fascinating and diverse group of languages that have evolved over centuries, originating from the Slavic tribes in Eastern Europe. These languages are spoken by over 300 million people worldwide. They are an important part of the cultural and linguistic heritage of many countries in Eastern Europe, the Balkans, and parts of Central Asia.
In this article, we will explore the 10 oldest Slavic languages, their history, and the unique features that have made them stand the test of time. Whether you’re a language enthusiast or simply curious about the evolution of Slavic languages, this article will provide you with a deeper understanding of the linguistic richness of this fascinating group of languages.
10. Serbian
Year Started: c. 1200s
No. of Speakers: 7.3 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Shtokavian, Torlakian, Ijekavian

Serbian is a South Slavic language that is primarily spoken in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and parts of Croatia, Kosovo, and North Macedonia. It is one of the official languages of Serbia and is also recognized as a minority language in several neighboring countries.
As a South Slavic language, Serbian belongs to the same branch of the Slavic language family as Bulgarian, Macedonian, and Slovenian. Serbian has several dialects, with the most prominent being Shtokavian, which is considered the standard dialect of the language. The other two major dialects are Torlakian and Ijekavian. These dialects have distinct features in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
Did You Know?
It has evolved over centuries from Old Church Slavonic, which was used as the liturgical language in the Balkans in the 9th century.
9. Russian
Year Started: 1100
No. of Speakers: 258 million
Classification: East Slavic
Major Dialects: Northern, Southern, Central

Russian is an East Slavic language that is primarily spoken in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. It is also widely spoken and understood in several other countries in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and the Baltic states. As an East Slavic language, Russian belongs to the same branch of the Slavic language family as Ukrainian and Belarusian.
It evolved from Old East Slavic, which was used in the Kievan Rus’ in the 10th to 13th centuries. Russian has several dialects, but the standard language is based on the Moscow dialect. It has a complex grammar system, with six cases and three genders.
Did You Know?
Russian vocabulary includes loanwords from other languages such as Latin, Greek, German, French, and English.
8. Croatian
Year Started: c. 1100s
No. of Speakers: 4.9 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Shtokavian, Kajkavian, Chakavian

Croatian is a South Slavic language that is primarily spoken in Croatia, as well as in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, and other neighboring countries. It is the official language of Croatia and one of the official languages of the European Union. As a South Slavic language, Croatian belongs to the same branch of the Slavic language family as Serbian, Bulgarian, and Macedonian.
Croatian has several dialects, with the Shtokavian dialect being the most widely used and considered the standard form of the language. Other dialects include Kajkavian and Chakavian. These dialects have distinct features in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Croatian is written using the Latin script, and it has a rich literary tradition with notable writers such as Miroslav Krleža, August Šenoa, and Ivana Brlić-Mažuranić.
Did You Know?
The language has a complex grammar system, with seven cases, three genders, and numerous verb tenses.
7. Bosnian
Year Started: c. 1100s
No. of Speakers: 1.7 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Shtokavian, Kajkavian, Chakavian
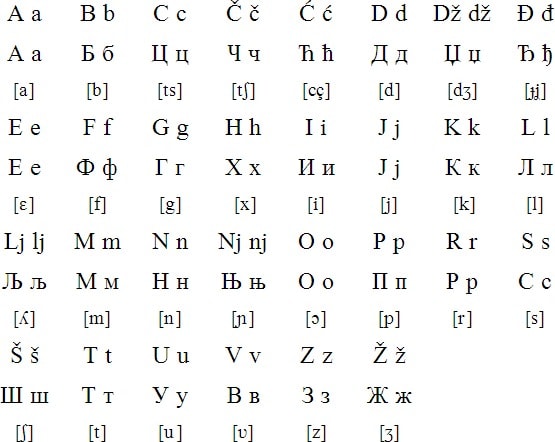
Bosnian is a South Slavic language that originated in the Balkans in the 1100s. Today, it is spoken by approximately 1.7 million people, primarily in Bosnia and Herzegovina but also in Serbia, Montenegro, and Croatia. Bosnian is closely related to other South Slavic languages, such as Croatian, Serbian, and Montenegrin, and shares many linguistic features with these languages.
It is also similar to Slovenian, which is another Slavic language spoken in the region. Bosnian has three major dialects: Shtokavian, Chakavian, and Kajkavian. Shtokavian is the most widespread and is used as the basis for the standard Bosnian language. Chakavian and Kajkavian are regional dialects that are spoken in specific parts of the country.
Did You Know?
In more recent times, the language has been influenced by the Croatian and Serbian languages due to their historical and cultural ties.
6. Ukrainian
Year Started: c. 1000s to 1300s
No. of Speakers: 32 million
Classification: East Slavic
Major Dialects: Cherkasyian, Poltavaian, Kyivian
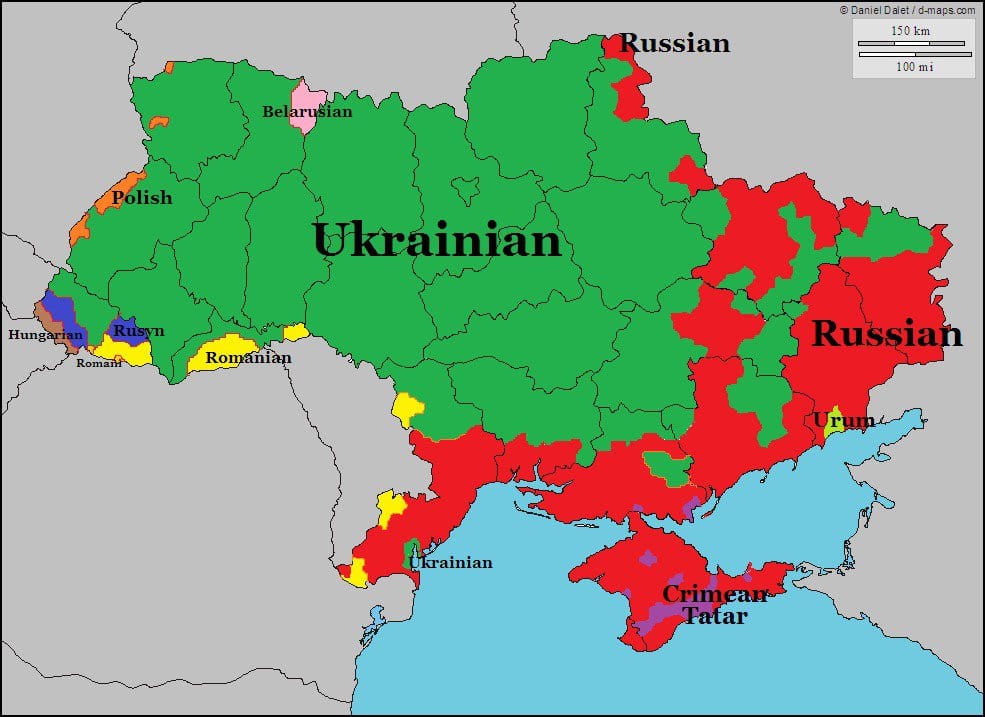
Ukrainian is an East Slavic language that originated in the 11th to 13th centuries in the region of Kievan Rus, which included parts of what is now Ukraine, Russia, and Belarus. Today, it is spoken by approximately 32 million people, primarily in Ukraine but also in neighboring countries such as Russia, Poland, and Romania.
The Ukrainian language has three major dialects: Cherkasyian, Poltavaian, and Kyivian. The Kyivian dialect is the basis for the standard Ukrainian language and is spoken in and around the capital city of Kyiv. The Ukrainian language has a rich literary tradition, with notable works dating back to the 12th century.
However, the language has faced challenges throughout its history, including periods of repression under Soviet rule. In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in the Ukrainian language and culture and efforts to promote the language and protect it from further marginalization.
Did You Know?
There are also differences in vocabulary and grammar between Ukrainian and Russian, despite the two languages sharing a common Slavic root.
5. Slovak
Year Started: 1000s
No. of Speakers: 5 million
Classification: West Slavic
Major Dialects: Eastern, Central, Western
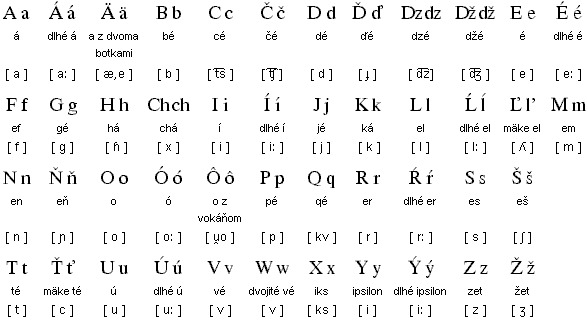
Slovak is a West Slavic language that originated in the 10th century in the region of Moravia, which is now part of the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Today, it is spoken by approximately 5 million people, primarily in Slovakia but also in neighboring countries such as the Czech Republic, Poland, and Hungary.
Slovak has three major dialects: Eastern, Central, and Western. The Eastern dialect is spoken in the eastern part of the country, while the Central dialect is spoken in the central regions, including the capital city of Bratislava. The Western dialect is spoken in the western part of the country, near the border with the Czech Republic.
Slovak is closely related to other West Slavic languages, such as Czech, Polish, and Sorbian, and shares many linguistic features with these languages. It also has some similarities with other Slavic languages spoken in Central and Eastern Europe, such as Slovenian and Croatian.
Did You Know?
Slovak has a relatively complex grammar system, with seven cases and three genders, and a rich vocabulary that includes many loanwords from other Slavic and non-Slavic languages.
4. Polish
Year Started: 1000s
No. of Speakers: Over 50 million
Classification: West Slavic
Major Dialects: Greater Polish, Lesser Polish, Masovian, Silesian

Polish is a West Slavic language that originated in the 10th century in the region of Greater Poland, which is now part of western Poland. Today, it is spoken by over 50 million people, primarily in Poland but also in other countries such as the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom.
Polish has four major dialects: Greater Polish, Lesser Polish, Masovian, and Silesian. The Greater Polish and Lesser Polish dialects are spoken in western and southern Poland, respectively, while the Masovian dialect is spoken in central Poland, including the capital city of Warsaw.
The Silesian dialect is spoken in the Silesian region of Poland, which borders the Czech Republic and Germany. It has a complex grammar system, with seven cases and three genders, and a rich vocabulary that includes many loanwords from other Slavic and non-Slavic languages.
Did You Know
It also has some similarities with other Slavic languages spoken in Central and Eastern Europe, such as Russian and Ukrainian.
3. Slovenian
Year Started: Between 972 and 1039
No. of Speakers: 2.5 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Gorenjska, Dolenjska, Štajerska, Panonska, Koroška, Primorska, Rovtarska

Slovenian is a language that emerged between 972 and 1039 in the Carantania region, now known as Slovenia. It is spoken by around 2.5 million individuals, mainly in Slovenia but also in neighboring countries such as Italy, Austria, and Hungary. The language has several major dialects, including Gorenjska, Dolenjska, Štajerska, Panonska, Koroška, Primorska, and Rovtarska, which are distinguished by their pronunciation and vocabulary.
The standard Slovenian language is based on the dialect spoken in the capital city of Ljubljana. Slovenian shares many linguistic features with other South Slavic languages like Croatian and Serbian and some similarities with other Slavic languages spoken in Central and Eastern Europe, such as Czech and Slovak.
Did You Know?
Slovenia has a rich literary tradition, and it played a significant role in the history and culture of Slovenia, including during periods of political and cultural repression under foreign rule.
2. Macedonian
Year Started: c. 9 CE to 1100s
No. of Speakers: 1.6 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Eastern groups, Western groups

Macedonian is a South Slavic language that originated in the region of Macedonia between 9 CE to 1100s and is currently spoken by around 1.6 million people, primarily in North Macedonia, with some speakers in neighboring countries. It has two major dialect groups, Eastern and Western, with the former being the basis of the standard Macedonian language. Macedonian shares similarities with Bulgarian and other South Slavic languages like Serbian, Croatian, and Slovenian.
It is written using the Cyrillic alphabet and has a complex grammar system with three genders, seven cases, and two numbers. The language has a rich vocabulary that includes many loanwords from other languages. Throughout history, Macedonian has been an important part of the cultural and literary heritage of North Macedonia, playing a crucial role in shaping the country’s national identity.
Did You Know?
In 1945, the Yugoslav government recognized Macedonian as a separate language from Bulgarian, leading to tensions between the two countries that persisted for many years.
1. Bulgarian
Year Started: c. 9 CE
No. of Speakers: 5.5 million
Classification: South Slavic
Major Dialects: Eastern groups, Western groups

Bulgarian is considered the oldest Slavic language because it has been spoken since the 9th century, making it the earliest Slavic language to emerge. It is a member of the South Slavic language group, which also includes Serbian, Croatian, and Slovenian. Bulgarian has a rich literary tradition, with notable authors including Hristo Botev, Ivan Vazov, and Geo Milev.
The language has a complex grammar system with six cases, three genders, and two numbers, which is typical of the Slavic languages. However, it also has some unique features, such as the absence of noun cases in the plural form and the use of a definite article. Bulgarian has two major dialect groups, Eastern and Western, which have some phonetic and grammatical differences. The Eastern dialect is considered to be the basis for the standard Bulgarian language.
Did You Know?
The Bulgarian language has contributed many loanwords to other languages, including Turkish, Greek, and Russian.