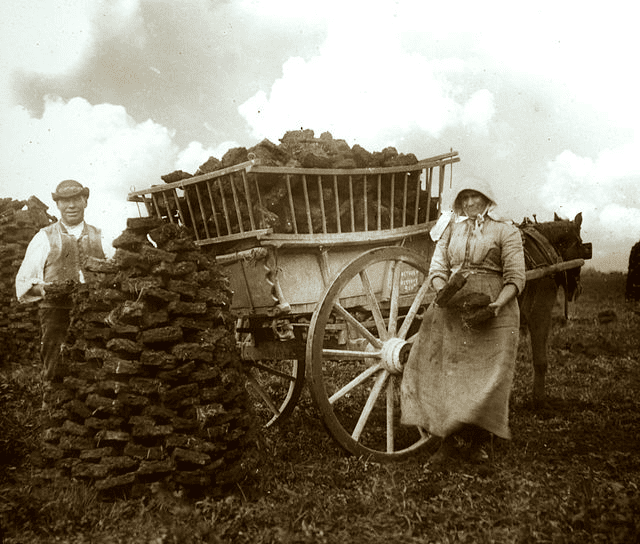
Coal, a vital fossil fuel that has fueled industrial revolutions and powered economies, has a long and storied history. While it’s well-known for its contributions to energy production, coal predates even the most ancient human civilizations.
In this article, we will explore the ten oldest and most significant varieties of coal, each with its own unique characteristics, history, and significance.
1. Anthracite Coal
Country: United States
Year: Anthracite has been mined in the United States since the early 19th century, with significant commercial production starting in the 19th century.
Anthracite is the hardest and most carbon-rich coal. It is often referred to as “hard coal” and has a remarkable ability to produce high heat with minimal impurities. Anthracite is valued for its high energy content and clean-burning properties.
Did You Know?
Anthracite is sometimes called the “black diamond” due to its lustrous, hard, and compact nature. It was a valuable fuel source during the American Civil War, providing heat for homes and industries.
2. Bituminous Coal
Country: Worldwide
Year: Bituminous coal has been used since the late 18th century, with commercial mining and widespread utilization beginning in the 19th century.
Bituminous coal is the most abundant coal widely used in electricity generation. It is known for its relatively high energy content, carbon concentration, and versatility in various industrial applications.
Did You Know?
Bituminous coal played a crucial role in the industrialization of Western nations during the 19th and early 20th centuries. It fueled steam engines, railways, and factories.
3. Sub-Bituminous Coal
Country: United States, China, Russia
Year: Sub-bituminous coal has been used for energy production since the late 19th century, with significant commercial mining operations.
Sub-bituminous coal is a lower-rank coal with a lower carbon content compared to bituminous coal. It is often used in power generation due to its moderate energy content and relatively low sulfur content, making it environmentally advantageous.
Did You Know?
In the United States, sub-bituminous coal is abundant in the Powder River Basin in Wyoming and Montana, making it a significant domestic energy source. Its lower sulfur content also makes it a cleaner-burning coal for power plants.
4. Lignite Coal
Country: Germany, Russia, United States
Year: Lignite has been mined and used for centuries, gaining prominence as a source of energy during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Lignite, often called “brown coal,” is the lowest-ranked coal with the lowest energy content. It is typically used in power plants due to its widespread availability and lower heating value.
Did You Know?
Lignite is characterized by its distinctly brownish-black color and lower energy content, but its abundance has made it a critical energy source in some regions.
5. Peat
Country: Worldwide
Year: Peat has been used for centuries, dating back to ancient civilizations. It is one of the earliest fuel and energy sources for human use.
Peat is an early stage of coal formation and consists of partially decayed plant material. It is not widely used for fuel but has applications in agriculture, particularly as a soil conditioner.
Did You Know?
Ireland is known for its extensive peat bogs, which have been historically used as a fuel source in some regions, especially in Northern Europe and parts of Asia.
6. Cannel Coal
Country: United Kingdom
Year: Cannel coal was extensively mined during the 19th century when oil production was in its infancy.
Cannel coal is a relatively rare variety known for its bright luster, fine texture, and high oil content. It was primarily used for fuel, particularly in oil production, during the 19th century.
Did You Know?
Cannel coal’s high oil content made it a valuable source of hydrocarbons for early oil production. It was known as “candle coal” because it could be used as a source of illumination when turned into oil.
7. Splint Coal
Country: United Kingdom
Year: Splint coal was mined and used during the 19th century, especially in the United Kingdom, where it was popular for residential heating.
Splint coal is a hard, brittle variety with a pronounced luster. Historically used for household heating and cooking, it is known for its clean-burning properties.
Did You Know?
Splint coal was favored for its relatively clean-burning properties, making it a preferred choice for household heating and cooking during the 19th century.
8. Jet Coal
Country: United Kingdom
Year: Jet coal has been used for thousands of years, particularly during the Victorian era when it was a popular material for jewelry and decorative items.
Jet coal, often referred to as “black amber,” is a type of lignite highly prized for its use in jewelry and ornamentation. It is valued for its smooth texture and ability to take a high polish.
Did You Know?
Jet coal’s smooth texture and deep black color made it a popular material for mourning jewelry during the Victorian era. It is also associated with spiritual and metaphysical properties.
9. Gondwana Coal
Country: India, Australia, Antarctica
Year: Gondwana coal formed during the Carboniferous and Permian periods, with mining dating back to ancient times when humans discovered its use as a fuel.
Gondwana coal is an ancient variety that dates back to the Gondwana supercontinent, which existed more than 300 million years ago. It represents coal deposits formed during the Carboniferous and Permian periods.
Did You Know?
Gondwana coal provides essential insights into the Earth’s geological history and the ancient vegetation that existed during its formation. It’s considered an invaluable geological record.
10. Carboniferous Coal
Country: Europe, North America
Year: Carboniferous coal was primarily formed during the Carboniferous period but has been mined since the 18th century when its use as a fuel source became widespread.
Carboniferous coal formed during the Carboniferous period, approximately 360 million years ago. It played a significant role in the development of coal resources, particularly during the Industrial Revolution.
Did You Know?
The Carboniferous period, also known as the “Age of Coal,” witnessed the extensive formation of coal deposits that are still extracted today. This coal was instrumental in powering early steam engines and the industrialization of Europe and North America.
Conclusion
The history of coal is a tale of human innovation, energy transformation, and geological time. These ten oldest varieties of coal have played pivotal roles in shaping our world, from powering the Industrial Revolution to serving as valuable resources for various industries.
As we continue to evolve and seek cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, it’s essential to acknowledge the significance and impact of these ancient fuels on our past and present.