The development of botanical gardens, which are primarily used for scientific research, is linked to the emergence of botany during the Renaissance. While using plants for medicinal purposes dates back to the early days of human history, the first true botanical gardens were not established until the 16th century. All of the oldest botanical gardens were created to be used by the major universities of the cities there were located in. The very first official botanical gardens were started in Italy and inspired the rest of Europe to establish their own gardens for research. Every botanical garden on this list is still operational today and is open to the local public for viewing.
9. University of Copenhagen Botanical Garden
Year Founded: 1600
Founder: Through a royal charter from Christian IV
Location: Copenhagen, Denmark
Area: 10 ha (24.7 acres)
Number of Plant Species: Over 13,000
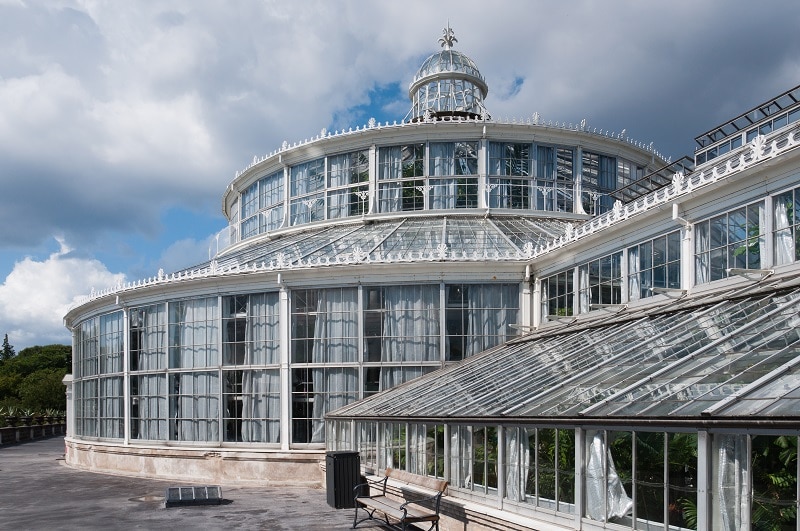

The University of Copenhagen Botanical Garden, typically called the Copenhagen Botanical Garden, was established in 1600 through a royal charter and land donated by Christian IV. A house for one of the university’s professors was also built on the garden grounds and it was up to that professor to care for the garden regardless of which chair they held. However, no funds were provided for the upkeep of the garden and it fell was not properly maintained until Ole Worm personally took it upon himself to restore the garden in 1621. Worm medicinal plants as well as rare foreign species.
The Copenhagen Botanical Garden was moved twice before being placed at its current location in 1870. The garden was widely expanded to accommodate the University’s extensive collection 1874 the gardens got its large complex of glasshouses at the initiative of Carlsberg founder J. C. Jacobsen who also funded it. Today, the Copenhagen Botanical Garden is known for these beautiful historic glasshouses and its collection of over 13,000 different plant species.
8. Jardin des plantes de Montpellier
Year Founded: 1593
Founder: King Henri IV, under the leadership of Pierre Richer de Belleval
Location: Montpellier, France
Area: 4.5 ha (11.12 acres)
Number of Plant Species: About 2,680
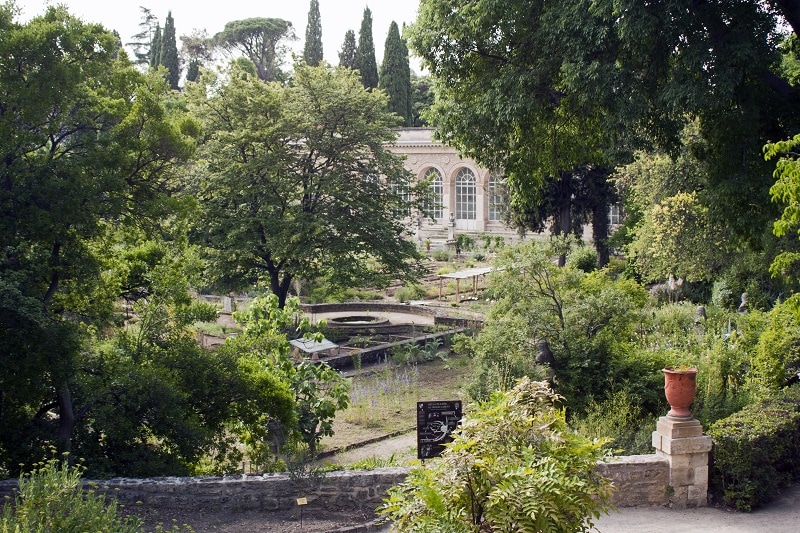

In 1593 King Henri IV of France tasked botanist Pierre Richer de Belleval with creating a Royal Garden that could be used for medicinal plant research. Belleval modeled the Jardin des plantes de Montpellier after the famed Botanical Garden of Padua – in turn, the Montpellier garden served as the model for the better-known Jardin des plantes de Paris. The Montepellier garden is the oldest botanical garden in France.
The oldest part of the garden is known as “Richer Mountain” and Richer de Belleval’s design inspired many later gardens throughout Europe. Unfortunately most of this part of the garden was destroyed during a siege in 1622. Following its destruction, Richer de Belleval expanded and redesigned the garden. It was updated and doubled in size once more during the 19th century. Today, the Jardin des plantes de Montpellier covers about 4.5 ha (11.12 acres) and houses more than 2,680 plant species.
7. Hortus botanicus Leiden
Year Founded: 1590
Founder: University of Leiden
Location: Leiden, Netherlands
Area: 3 ha (7.5 acres)
Number of Plant Species: Over 10,000
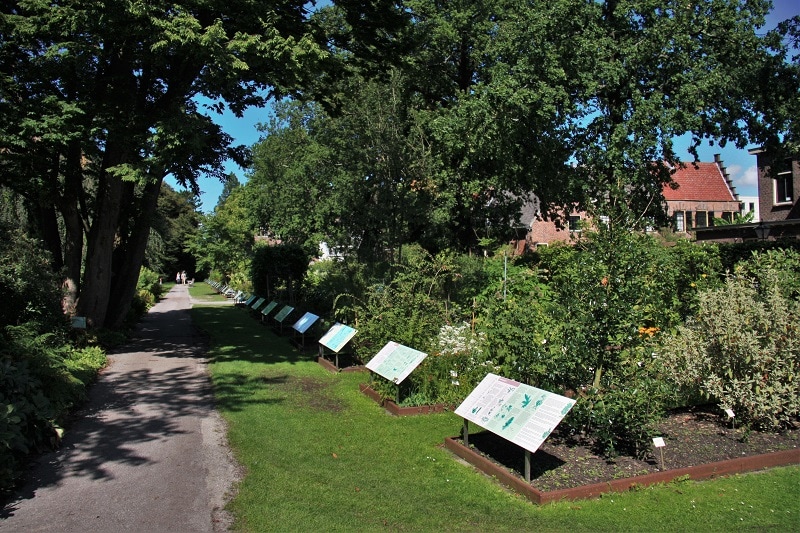

The idea to start an academic garden at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands started in 1587 when the University asked the city’s mayor to create a place where the medical students could study medicinal plants. The Hortus botanicus of Leiden was finally opened in 1590 and famous botanist Carolus Clusius was appointed as the garden’s prefect. Clusius used his international contacts to set up an extensive plant collection and he also asked the Dutch East India Company to collect plants and dried plant specimens from Dutch colonies around the world.
Throughout its long history, the Hortus bontaicus was continuously expanded with the addition of new greenhouses and exotic plant collections. In the scientific community, the Hortus botanicus Leiden is known for its collection of Asian Araceae as well as having one of the largest collection of Asian orchids in the world.
6. Botanischer Garten Jena
Year Founded: 1586
Founder: Medical Faculty of the University of Jena
Location: Jena, Thuringia, Germany
Area: 4.5 ha (11.12 acres)
Number of Plant Species: About 12,000
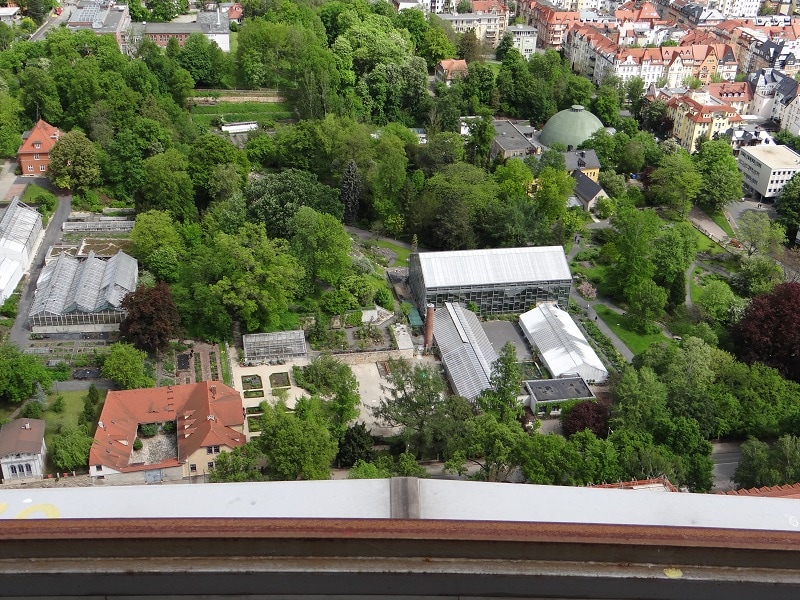

The Botanischer Garten Jena or Jena Botanical Garden in English is the second oldest botanical garden in Germany. The garden of was founded in 1586 by the Medical Faculty of the University of Jena and was initially operated as a “Hortus Medicus” where the school could study medicinal plants and their uses.
The garden’s first major expansion took place in 1630 under the direction of Professor Werner Rolfnick, who had been working for several years at the Padua Botanical Garden in Italy (the second oldest botanical garden in the world). Today, the Jena Botanical Garden covers an area of 4.5 hectares (11.12 acres) and by the adjoining biological, pharmaceutical and botanical institutes and the population for education and recreation. There are about 12,000 different plants in greenhouses and outdoor spaces and the Jena Botanical Garden is open to the public.
5. Leipzig Botanical Garden
Year Founded: 1580 – but as early as 1542
Founder: Unknown – possibly the Dominican monastery of St. Pauli
Location: Leipzig, Saxony, Germany
Area: 3.5 ha (8.65 acres)
Number of Plant Species: About 7,000

The Leipzig Botanical Garden, which is maintained by the University of Leipzig in Germany, is considered to be the oldest botanical garden in Germany. According to the history of the garden, it traces its origins back to 1542 when the Dominican monastery of St. Pauli, which was known for its beautiful garden, was transferred to the University. While it is uncertain, it is believed that the school may have maintained it as a medicinal plant garden.
The official founding date of the University’s garden is usually cited as 1580. However, over the next 450 years the garden was moved four times throughout the city due to various reasons, including its total destruction during World War II. The garden was moved to its current location in 1876 and was completely renovated between 1992 – 2004, following Germany’s reunification.
4. Botanical Garden of the University of Valencia
Year Founded: as early as 1567 – current site in 1802
Founder: Municipal government of the City of Valencia
Location: Valencia, Spain
Area: Unknown
Number of Plant Species: Unknown
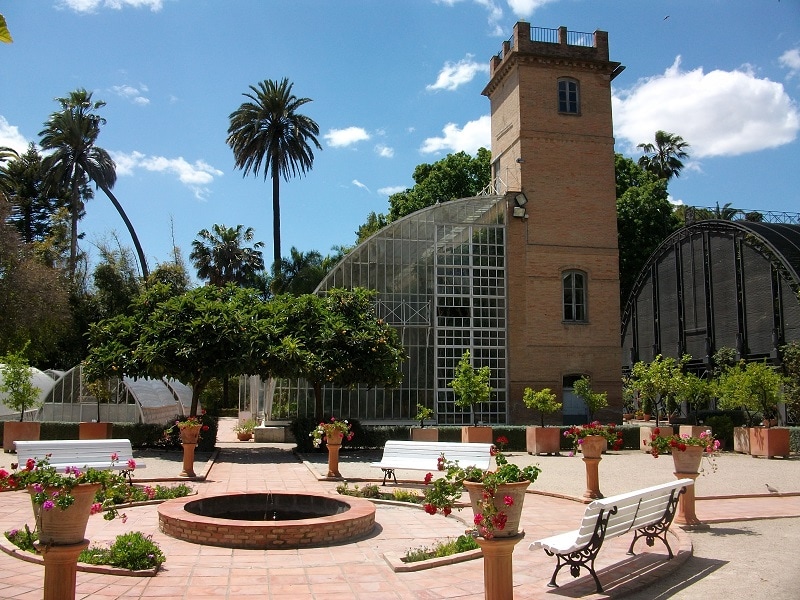

The origins of the Botanical Garden of the University of Valencia are hard to trace, but it is widely believed that the University first formally started growing medicinal plants sometime in the 16th century. In 1548, the University established a chair of medical practice and in 1560, started teaching separate classes about medicinal plants. A few years later, the municipal government appointed Joan Plaça as doctor of medicine and gave him a small garden to grow plants that would be used for teaching – no one knows where this original garden was located.
The current Botanical Garden of the University of Valencia was established in 1802 when the city finally granted the University land to build their new garden. Over the next few centuries, the garden was destroyed several times due to war and a destructive flood in 1957. Extensive reconstruction of the garden took place in the 1960s and a new research building was constructed in 2000. Today, the Botanical Garden of the University of Valencia is part of Botanical Gardens Conservation International (BGCI), which is the world’s largest plant conservation network.
3. Orto botanico di Firenze
Year Founded: December 1, 1545
Founder: Cosimo I de’ Medici
Location: Florence, Italy
Area: 2.39 ha (5.9 acres)
Number of Plant Species: About 9,000
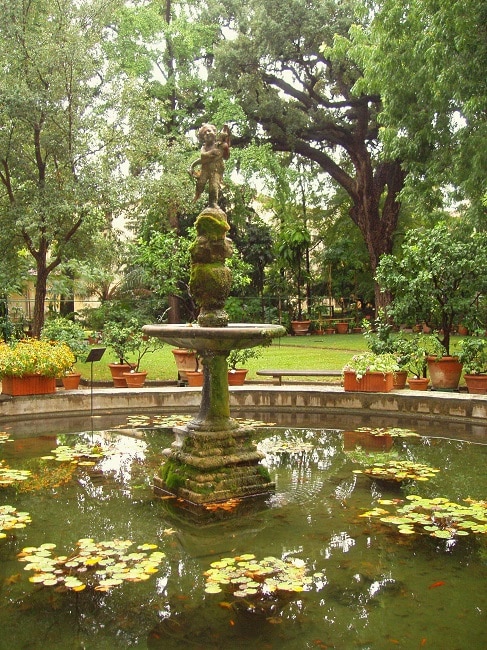

The Orto botanico di Firenze was opened in late 1545 and is officially the third oldest botanical garden in the world. Like the botanical garden in Pisa, the Orto botanico di Firenze was founded by Cosimo I de’ Medici, the Grand Duke of Tuscany. In line with all of the early botanical gardens, the Florence gardens were used to cultivate medicinal plants.
The original layout of the Orto botanico di Firenze was designed by landscape gardener Niccolò Pericoli. The director of the Pisa botanical gardens, botanist Luca Ghini was initially in charge of the Orto botanico di Firenze. The garden was heavily improved in the 18th century thanks to Cosimo III dei Medici and the direction of famous botanist Pier Antonio Micheli. Today, the garden covers an area of about 2.39 hectares and is home to several very old trees, including one planted by Micheli in 1720.
2. Orto botanico di Padova
Year Founded: 1545
Founder: Senate of the Venetian Republic
Location: Padua, Italy
Area: 2.2 ha (5.4 acres) (22,000 square meters)
Number of Plant Species: Over 6,000
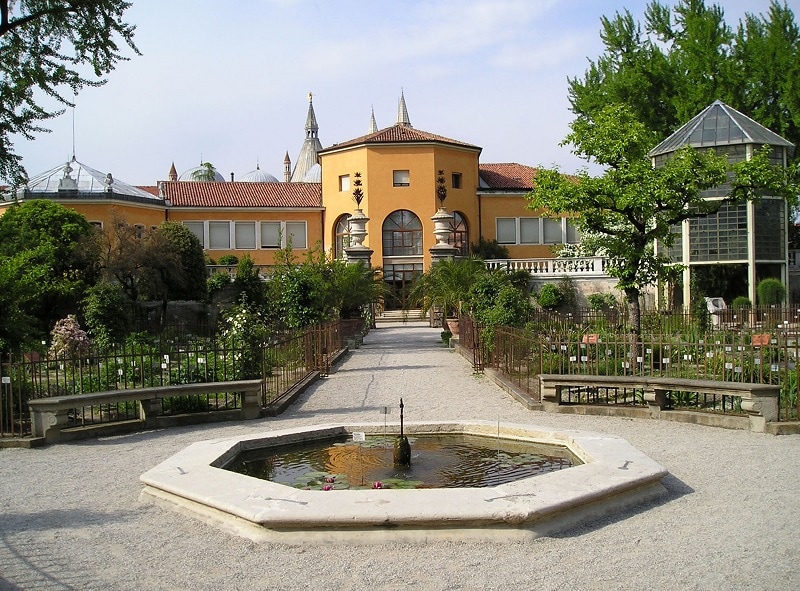

Although the botanical garden run by the University of Pisa was opened first, the Orto botanico di Padova is often cited as the world’s oldest academic botanical garden because it has never moved from its original location. The garden, which has always been affiliated with the University of Padua, was first built in 1545 by the Senate of the Venetian Republic. They wanted to use the garden to grow medicinal plants which produced natural remedies, and also to help students distinguish genuine medicinal plants from false ones.
The Orto botanico di Padova was designed by Italian architect Daniele Barbaro. Inspired by medieval enclosed gardens, Barbaro marked the architecture by a perfect pattern of a square within a circle, divided into four parts by two paths oriented according to the cardinal points. There are currently over 6,000 types of plants being cultivated at the gardens, including several rare species. In 1997, the Orto botanico di Padova was listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
1. Orto botanico di Pisa
Year Founded: 1544
Founder: Cosimo I de’ Medici and run by botanist Luca Ghini
Location: University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
Area: Unknown
Number of Plant Species: Unknown
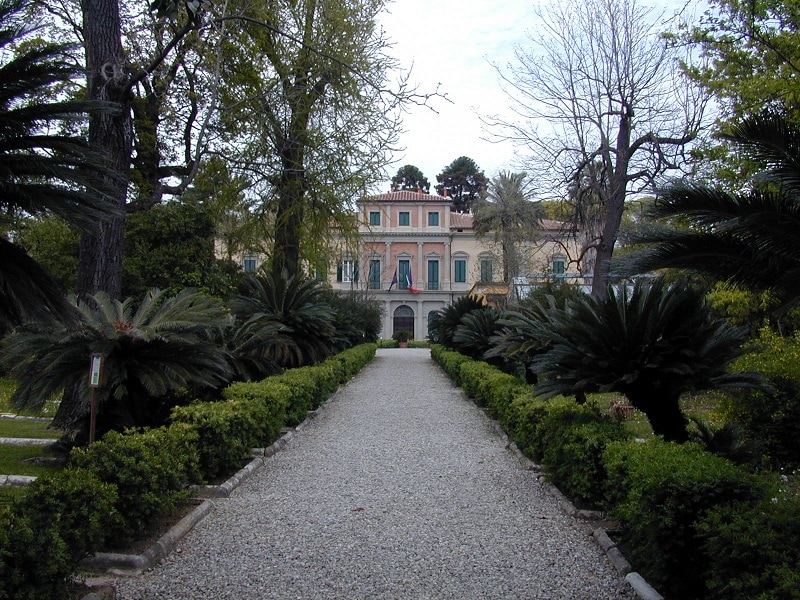

The botanical garden operated by the University of Pisa in Italy, which is known as the Orto botanico di Pisa, was the world’s first true botanical garden. The Orto botanico di Pisa was established in 1544 under the rule of Cosimo I de’ Medici to serve as the research facility for famed botanist Luca Ghini, making it the oldest botanical garden in the world. One of Ghini’s greatest innovations was to establish an herbarium at the botanical garden where he dried plants so he could study them throughout the off-season.
The Orto botanico di Pisa was initially located on the banks of the river Arno, but was moved in 1563 near the convent of Santa Maria. Under the direction of Flemish botanist Joseph Goedenhuyze, the Orto botanico di Pisa was moved to its current location in 1591 and was slowly expanded throughout the years. Today, the garden is divided into sections containing the botanical school, gardens, ponds, greenhouses, and various buildings.