Technically speaking, there is only one World Ocean (since the Earth’s oceanic waters are all connected), but this singular ocean has been divided into five different “oceans” – the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Arctic Ocean, and Southern Ocean (Antarctic). Due to plate tectonics, post-glacial rebound, and sea level rise the structure of the world’s ocean is constantly changes. To determine the current age of the oceans, the oldest parts of their ocean floors have been measured, which all vary, but are generally less than 200 million years old.
5. Southern Ocean (Antarctic)
Current Age: c.30 million years
Surface Area: 7,849,000 sq mi (20,328,817 km²)
Volume: 17,225,736 cu mi (71,800,000 km³)
Average Depth: 10,728 ft (3,270 m)
Max Depth: 24,390 ft (7,434 m)
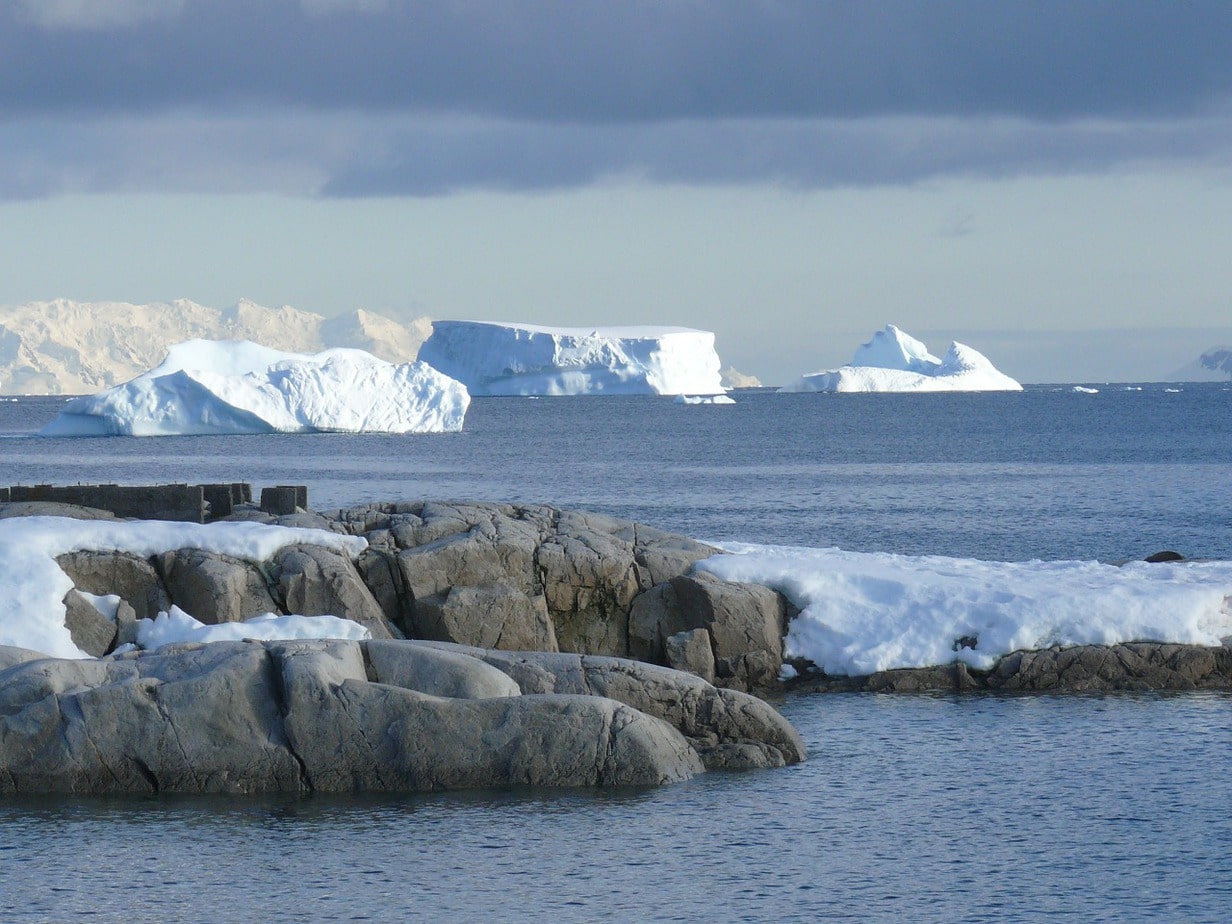

The Southern Ocean or Antarctic Ocean is not only the youngest ocean – it formed roughly 30 million years ago – but it is also the “newest” named ocean basin. However, not all scientists and geographers agree that the Southern Ocean should even count as a separate region because various parts of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans exist within the realms of what has been appointed the Southern Ocean by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO).
After the Arctic Ocean, the Southern Ocean is the next smallest, covering an area of about 7,849,000 square miles (20,328,817 square kilometers). While the Southern Ocean is smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, it’s quite deep with an average depth of 10,728 feet (3,270 meters). The maximum depth of the Southern Ocean was only recorded recently in early 2019. The research team measured the Southern Ocean’s max depth at 24,390 feet (7,434 meters).
Did You Know?
The icebergs that form in the Southern Ocean are so large that they contain enough fresh water to sustain every person on Earth for several months.
4. Arctic Ocean
Current Age: between 80 million to 67 million years
Surface Area: 6,100,000 sq mi (15,799,186.47 km²)
Volume: 4,498,364 cu mi (18,750,000 km³)
Average Depth: 3,406 ft (1,038 m)
Max Depth: 17,880 ft (5,450 m)
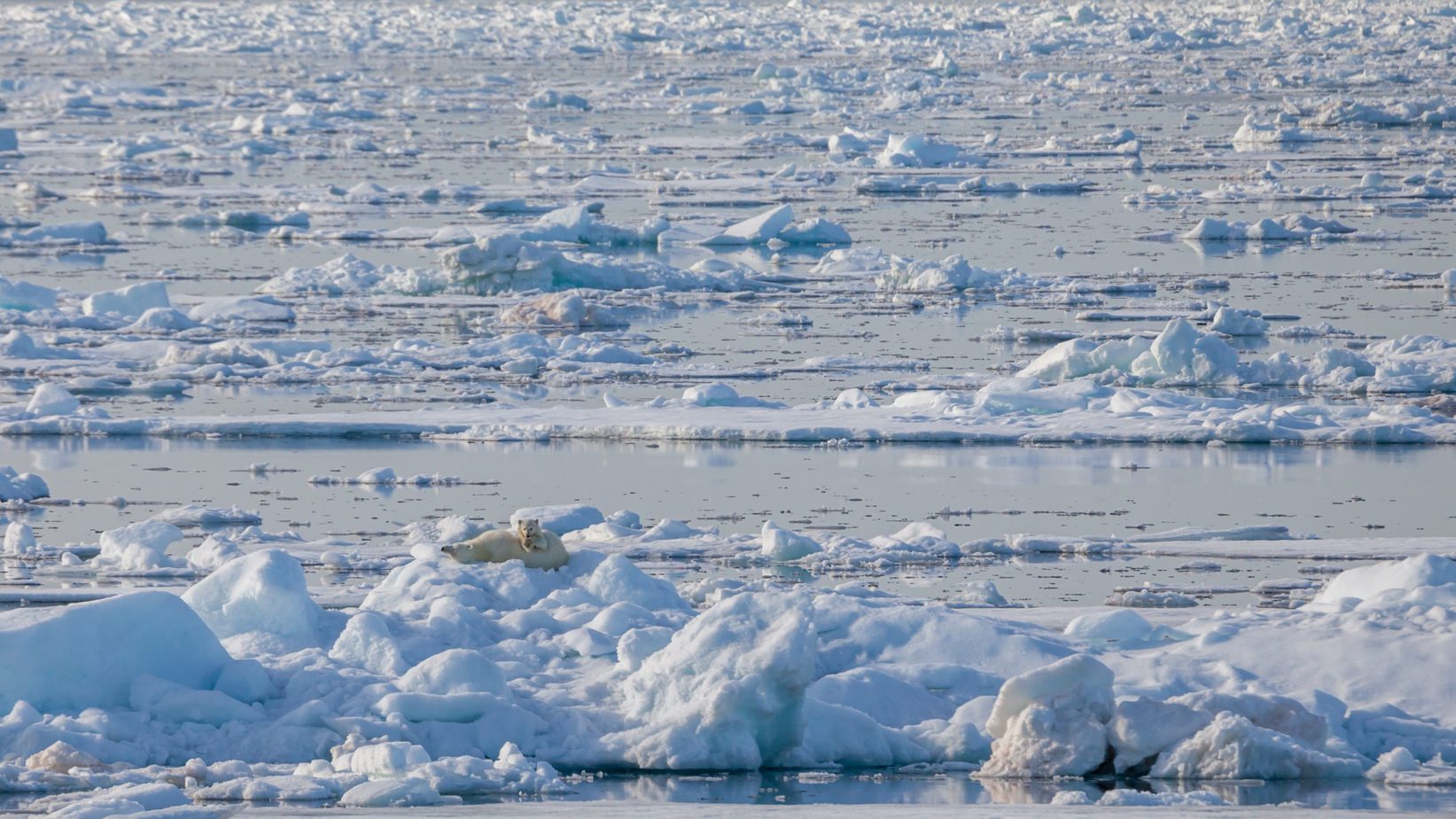

For most of the year, the Arctic Ocean is completely covered in ice and average temperatures usually do not rise above freezing. Unfortunately, the Arctic Ocean has been heating up and melting due to extreme climate changes caused by human activities. According to several reports, the Arctic is heating up twice as fast as the global averages. The continued warming of the Arctic Ocean will heavily impact life around the world for people, plants, and animals.
Although the area around the Arctic Ocean is so cold about four million people call the region home. The U.S., Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, and Russia all have territories that reach into the Arctic Ocean. Because much of the Arctic Ocean is dark and covered by ice, a majority of this ocean and its marine life and plants remain a mystery.
Did You Know?
During the winter, the polar ice of the Arctic Ocean can measure as thick as 164 feet (about 50 meters).
3. Indian Ocean
Current Age: less than 150 million years
Surface Area: 27,240,000 sq mi (70,560,000 km²)
Volume: 63,000,000 cu mi (264,000,000 km³)
Average Depth: 12,274 ft (3,741 m)
Max Depth: 23,812 ft (3,741 m)

After the Pacific and Atlantic, the Indian Ocean is the world’s third largest and oldest ocean. The Indian Ocean began forming less than 150 million years ago and the oldest part of its ocean floor dates back to around this time. However, a majority of the Indian Ocean basin is less than 80 million years old. The continent of Asia borders the Indian Ocean to the north, while Africa borders it to the west, and Australia is on its eastern border.
The Indian Ocean covers an area of about 27,240,000 square miles (70,560,000 square kilometers), which amounts to about 19.8% of the Earth’s surface. The deepest part of the Indian Ocean is the Java or Sunda Trench, which is 23,812 feet (3,741 meters) deep.
In the West, the Indian Ocean has had its name since at least 1515 and is derived from the the Greek/Roman name for the “region of the Indus River.” The Ancient Indians called this body of water the Sindhu Mahasagara or the great sea of the Sindhu. It has also been called the Hindu Ocean, Indic Ocean, Eastern Ocean, and “Western Ocean” by Chinese explorers in the 15th century.
Did You Know?
The Indian Ocean is the warmest ocean basin in the world. It is so warm that the growth of phytoplankton is limited, which in turn limits the native marine animals in the Indian Ocean’s waters.
2. Atlantic Ocean
Current Age: c.150 million years
Surface Area: 41,100,000 sq mi (106,460,000 km²)
Volume: 74,471,500 cu mi (310,410,900 km³)
Average Depth: 11,962 ft (3,646 m)
Max Depth: 27,480 ft (8,376 m)

The Atlantic Ocean is second largest and oldest ocean, following the Pacific Ocean – it is only slightly larger than half the size of the Pacific and several million years younger. Covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface, the Atlantic separates the continents of Europe and Africa to the east from those of North and South America to the west. Throughout history, the Atlantic is also the bridge between the “Old World” (Africa, Asia, and Europe) and the “New World” (the Americas).
Because the Atlantic Ocean borders Africa, some of the earliest evidence of human activity are found along several Atlantic coastal areas. There are many shell middens (dumping areas for waste, in this case mollusc shells) that date back to the earliest days of our human ancestors.
While the Atlantic Ocean has an average depth of about 11,962 feet (3,646 meters), its deepest point is 27,480 feet (8,376 meters) in the Puerto Rico Trench, located just north of Puerto Rico. Typically, the Atlantic Ocean is separated into the North Atlantic and South Atlantic by scientists and geographers. The North Atlantic and South Atlantic have distinct characteristics that affect the world’s weather – the norther water of the Atlantic are known to be much colder while the South Atlantic is more tropical, especially in the Caribbean.
Did You Know?
The oldest known written records of the Atlantic Ocean come from Greek poet Stesichorus around mid-sixth century BCE in his work Atlantikoi peláge (‘the Atlantic Sea’ or ‘Sea of Atlantis’) and in The Histories of Herodotus around 450 BCE where he mentions Atlantis thalassa (which has the same meaning as the name of Stesichorus’ poem). In both instances, the name of the ocean refers to Atlas, a Titan from Greek mythology.
1. Pacific Ocean
Current Age: c.180 million years
Surface Area: 63,800,000 sq mi (165,250,000 km²)
Volume: 170,000,000 cu mi (710,000,000 km³)
Average Depth: 14,040 ft (4,280 m)
Max Depth: 35,797 ft (10,911 m)

In addition to being the oldest part of the World Ocean, the Pacific is deeper and larger than the other oceans, covering over 46% of Earth’s water surface and about one-third of its total surface area. This makes the Pacific Ocean larger than all of Earth’s land area combined.
Sometimes, the Pacific Ocean is called the Pacific Ring of Fire because of the earthquake and volcanic activity around the ocean’s edges. The chain of volcanoes in the Ring of Fire is about 25,000 miles long and consists of about 452 volcanoes (more than 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes).
Besides hundreds of volcanoes, the Pacific Ocean is also home to about 25,000 islands and it borders many countries and territories. Some of the countries bordering the Pacific include: The United States, Fiji, Mexico, Vietnam, the Philippines, Canada, Russia, Chile, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, and many more.
Did You Know?
The Pacific Ocean was named by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan after he entered an ocean he was not familiar with. Magellan called the waters pacific, which means peaceful, because of how calm they were at the time.