While the Roman Empire was one the longest empires (lasted about 1,500 years) and is probably the most famous, in the span of human history, it is fairly modern. The earliest empires precede the Roman Empire by over 2,000 years.
These early empires were formed by the early civilizations of Ancient Mesopotamia and the surrounding areas. As these civilizations grew, so did their sphere of power and their desire to conquer near and distant lands.
Many of these first empires ruled over the same lands, eventually replacing one another as they fell.
8. Achaemenid Empire
Year Established and Ended: c.550 BCE – 330 BCE
Duration: 220 years
Founding Country: Ancient Near East (modern-day Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran, northeastern Syria, and Kuwait)
Capital City: Several, but Babylon was the main capital
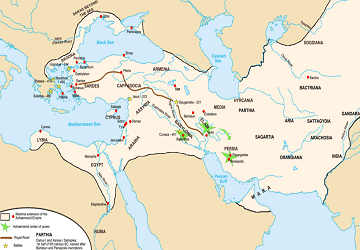

The Achaemenid Empire was the first Persian Empires and one of the largest empires ever in history. The empire was founded around 550 BCE by Cyrus the Great. Under his rule the empire expanded from the Ancient Near East to most of Southwest Asia, much of Central Asia, and the Caucasus, making it a larger empire than any previous empire.
In addition to its military prowess, the Achaemenid Empire is notable for its successful model of a centralized, bureaucratic administration, for building infrastructure such as road systems as well as a postal system, the use of an official language across its territories, and the development of civil services.
The decline of the empire is attributed to heavy tax burdens and the failure to create a national identity among its subjects from different nations.
7. Carthaginian Empire
Year Established and Ended: 650 BCE – 146 BCE
Duration: 504 years
Founding Country: North Africa
Capital City: Carthage
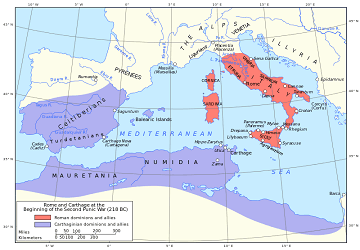

The Phoenician city-state of Carthage was founded in 814 BCE. It gained its independence in 650 BCE and established its control over the other Phoenician settlements in the western Mediterranean — this was the start of the Carthaginian Empire.
At its peak, the empire’s capital city of Carthage served as a major trading hub and was called the “shining city”, which ruled over 300 other cities.
Throughout most of the empire’s history, it was at war with the Greeks in Sicily as well as the Roman Republic.
These hostilities led to a series of armed conflicts known as the Greek-Punic Wars (c.600 BCE – 265 BCE) and the Punic Wars (264 BCE – 146 BCE). After the third and final Punic War sometime in 146 BCE, Carthage fell to the Roman Republic.
6. Kushite Empire (Nubian Dynasty)
Year Established and Ended: 760 BCE – 656 BCE
Duration: 94 years
Founding Country: Ancient Egypt ruled by the Nubians from the Kingdom of Kush (modern-day northern Sudan and southern Egypt)
Capital City: Napata
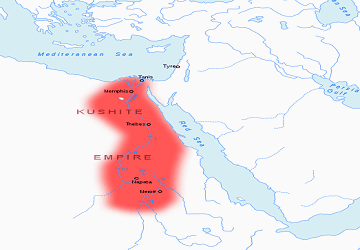

The Kushite Empire, also known as the 25th Dynasty of Egypt and the Nubian Dynasty, occurred when the Nubians successfully invaded Ancient Egypt. The first king of the Kushite Empire was Piye, whose father Kashta had started the invasion of Upper Egypt. Their war brought together Upper Egypt, Lower Egypt, and Kush, forming the largest Egyptian empire since the New Kingdom (c.1550 BCE – c.1077 BCE).
Under Piye, the construction of pyramids was revived and he built the oldest pyramid at the royal burial site of El-Kurru and also expanded the Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal.
The rulers after Piye also took interest in restoring Egyptian monuments and building some of their own. They attempted to regain parts of Egypt from the Assyrians, but were unsuccessful.
5. Egyptian Empire (New Kingdom of Egypt)
Year Established and Ended: c.1550 BCE – c.1077 BCE
Duration: 473 years
Founding Country: Ancient Egypt
Capital City: Several cities throughout duration: Thebes, Akhetaten, Thebes again, Pi-Ramesses, and Memphis
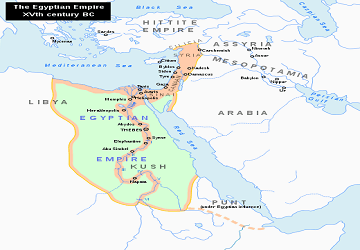

Although the ancient Egyptians had first established its kingdom around 2686 BCE, the New Kingdom is the only era known as the Egyptian Empire. This period of ancient Egyptian history spans over the 18th, 19th , and 20th Dynasties of Egypt, which lasted from around 1550 BCE until 1077 BCE.
During the Egyptian Empire, Egypt was at the height of its power and prosperity.
Some of Egypt’s most well-known Pharaohs ruled during this time including Ahmose I, Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, Amenhotep III, Akhenaten, Tutankhamun, and Ramesses II (“the Great”).
Also under the Egyptian Empire, art and architecture flourished. The Valley of the Kings was built around this time — it is Egypt’s largest funerary complex containing the tombs of several Pharaohs and powerful nobles.
4. Hittite Empire
Year Established and Ended: c.1600 BCE – 1178 BCE
Duration: 422 years
Founding Country: north-central Anatolia (parts of modern-day Turkey)
Capital City: Hattusa
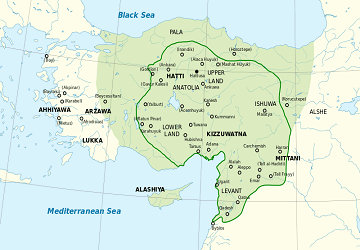

The Hittite Empire was established sometime around 1600 BCE and at its peak, encompassed most of Anatolia as well as parts of northern Levant (modern-day Syria) and Upper Mesopotamia (northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria, and southeastern Turkey).
Due to its geographic location, the Hittite Empire often came into fought with the Egyptian Empire, the Middle Assyrian Empire, and the Kingdom of Mitanni for control of the area.
Eventually, the Assyrians dominated the area and annexed most of the Hittite Empire’s lands. With so much competition from surrounding empires, the Hittite Empire had several weak periods with insignificant rulers and reduced areas of control. Not much about these weaker periods is known because the Hittites kept less precise records during these times.
3. Babylonian Empire (First Babylonian Dynasty)
Year Established and Ended: c.1894 BCE – c.1595 BCE
Duration: 300 years
Founding Country: central-southern Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq)
Capital City: Babylon
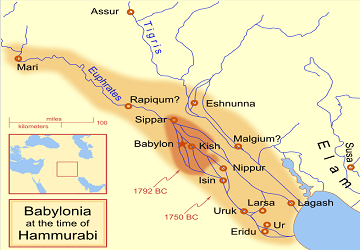

The First Babylonian Dynasty lasted from about 1894 BCE – 1595 BCE. This first era in the Babylonian Empire emerged when an Amorite (a Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the northern Levant — the historical region of Syria) king established a small kingdom that included Babylon, which was a minor town at the time.
Eventually, Babylon grew in size and power and reached its peak under the reign of Hammurabi (c. 1728—1686 BCE).
After Hammurabi’s death, the Babylonian Empire began to rapidly decline and eventually reverted back into a small kingdom. Sometime around the end of the First Babylonian Dynasty, the capital city of Babylon was sacked by the Hittites under king Mursili I.
2. Assyrian Empire
Year Established and Ended: c.2025 BCE – c.605 BCE
Duration: 1,420 years
Founding Country: Assyria (parts of modern-day Iraq, Turkey, Syria, and Iran)
Capital City: several throughout different periods – first capital city was Aššur
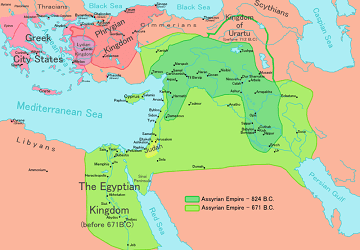

The Assyrian Empire is typically divided into four eras: the Early Assyrian Period, the Old Assyrian Empire, the Middle Assyrian Period, and the New Assyrian Period. Although the first capital city of Aššur was first established around 2600 BCE, during the Early Period, Assyrians were under the rule of the Akkadian Empire.
While it was a kingdom during this time, the Assyrian Empire did not emerge until after the fall of the Akkadian Empire. During the height of the Assyrian Empire, it ruled over what the ancient Mesopotamian religion called the “Four Corners of the World”: as far north as the Caucasus Mountains, as far east as the Zargos Mountains, as far west as Cyrpus in the Mediterranean Sea, and as far south as the Arabian desert.
1. Akkadian Empire
Year Established and Ended: c.2334 BCE – c.2154 BCE
Duration: 180 years
Founding Country: Ancient Mesopotamia – around modern-day Iraq
Capital City: Akkad

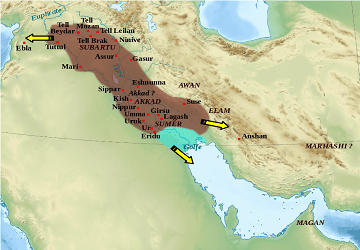
The Akkadian Empire was the first empire of ancient Mesopotamia, which makes it the oldest empire in the world. Under the empire, Akkadians and Sumerians were united and many people were bilingual, speaking both the Akkadian and Sumerian language.
There were eight kings over the duration of the Akkadian Empire: Sargon, Rimush, Manishtushu, Naram-Sin, Shar-Kali-Sharri, Interregnum, Dudu, and Shu-turul.
Although scholars have documented over 7,000 texts detailing the Akkadian Empire, they have not yet located the capital city of Akkad.
Most of the archaeological research related to the Akkadian Empire comes from an area in modern northeastern Syria, which became part of Assyria after the fall of Akkad. Now Iraq is one of the early-formed countries in the world.
OTHER POSTS YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN











it’s so fascinating to learn about the empires of our time and all the different things about them. including the order of which they lasted and how old they are.