In general, all constitutions are basically the same. Constitutions outline the legal systems of a country and also detail its citizens’ rights. Many of the world’s constitutions were originally written a few centuries ago, but have been amended over the years when necessary.
This list contains some of the world’s oldest constitutions, which have been in continuous (with many revisions and amendments) use since they were first written.
10. Constitution of Canada
Date Ratified: July 1, 1867
Last Amended: 1982
Author(s): Canadian Confederation
Government Type: Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy

While Canada is a self-governing nation, it still remains a British Commonwealth country today.
Canada’s Constitution outlines the country’s system of government, including the structure of its Parliament, the way elections work, the role of the monarchy, and the divisions of powers between the federal government and the provinces.
The Constitution was last updated in 1982, which included a long section known as the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which outlines the civil rights of each Canadian citizen. The 1982 Act also describes the process for amending constitutional laws.
Did You Know?
In the 1980s and 1990s, Canada unsuccessfully tried to amend the Canadian Constitution, which has now made the subject of fixing the Constitution an unpopular political topic.
9. Constitutional Act of the Kingdom of Denmark
Date Ratified: June 5, 1849
Last Amended: June 5, 1953
Author(s): D.G. Monrad and Orla Lehmann
Government Type: Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy

Like many of the countries on this list, the Kingdom of Denmark is both a monarchy and democracy. As a constitutional monarchy, the power of the monarch is limited by the Constitutional Act of the Kingdom of Denmark, which dates back to 1849.
The Constitutional Act is the most important piece of legislation in Denmark, and all other laws must comply with it.
The Constitutional Act was last amended on June 5, 1952. The original Act from 1849 was 100 sections, but was cut down to 89 sections, grouped into 11 chapters.
Not only does the Constitutional Act outline Danish democracy, it also establishes the rights and duties of individual citizens, such as freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and compulsory military service.
Did You Know?
Denmark moved from an absolute monarchy to a constitutional monarchy after King Christian VIII — before he died — ordered his son, Frederik VII to promise the Danish people a new constitution that guaranteed them freedom and equality and prevented any one person from having unlimited power.
8. Swiss Federal Constitution
Date Ratified: September 12, 1848
Last Amended: May 8, 2014
Author(s): Federal Assembly
Government Type: Federal semi-direct democracy under a multi-party assembly-independent directorial republic

The Swiss Federal Constitution was first written on September 12, 1848 and it established the Swiss Federal State. Switzerland was heavily influenced by the United States Constitution as well as the ideals of the French Revolution.
To write up the Swiss Federal Constitution, a Federal Aseembly, a bicameral assembly consisting of the National Council and Council of States, was established.
Additionally, the Swiss Federal Constitution provided its citizens with a declaration of fundamental individual rights, a federal government, and a federal court of justice.
This 1848 Constitution was later rewritten in 1874. The modern Swiss Federal Constitution was ratified on April 18, 1999 and directly replaced the 1874 Constitution.
Did You Know?
The Swiss Federal Constitution designated Bern (of Berne) as Switzerland’s capital city.
7. Constitution of Luxembourg
Date Ratified: October 12, 1841
Last Amended: October 18, 2016
Author(s): William II
Government Type: Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy

The Constitution of Luxembourg was first written in 1841, just two years after Luxembourg became a sovereign nation. The current Constitution dates to 1868 and it was last amended in 2016. Luxembourg’s Constitution consists of 121 articles, divided into 13 chapters.
Similar to every other constitution, Luxembourg’s Constitution describes the constituent foundations of the State, the guarantee of the rights and liberties of the nation’s citizens, and the organization of the powers.
While the Constitution of Luxembourg has been revised several times since 1841, one of the biggest changes took place in 1919.
Following that revision of the Constitution, all citizens of legal age, 21 at the time (lowered to 18 in 1972), were given the right to vote. Before this, only males aged 25 and older who paid a certain amount of tax were allowed to vote.
Did You Know?
According to Luxembourg’s official website, its Parliament is currently in the process of recasting, or updating it to reflect a modern democracy.
6. Constitution of Belgium
Date Ratified: February 7, 1831
Last Amended: 1993
Author(s): National Congress
Government Type: Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy
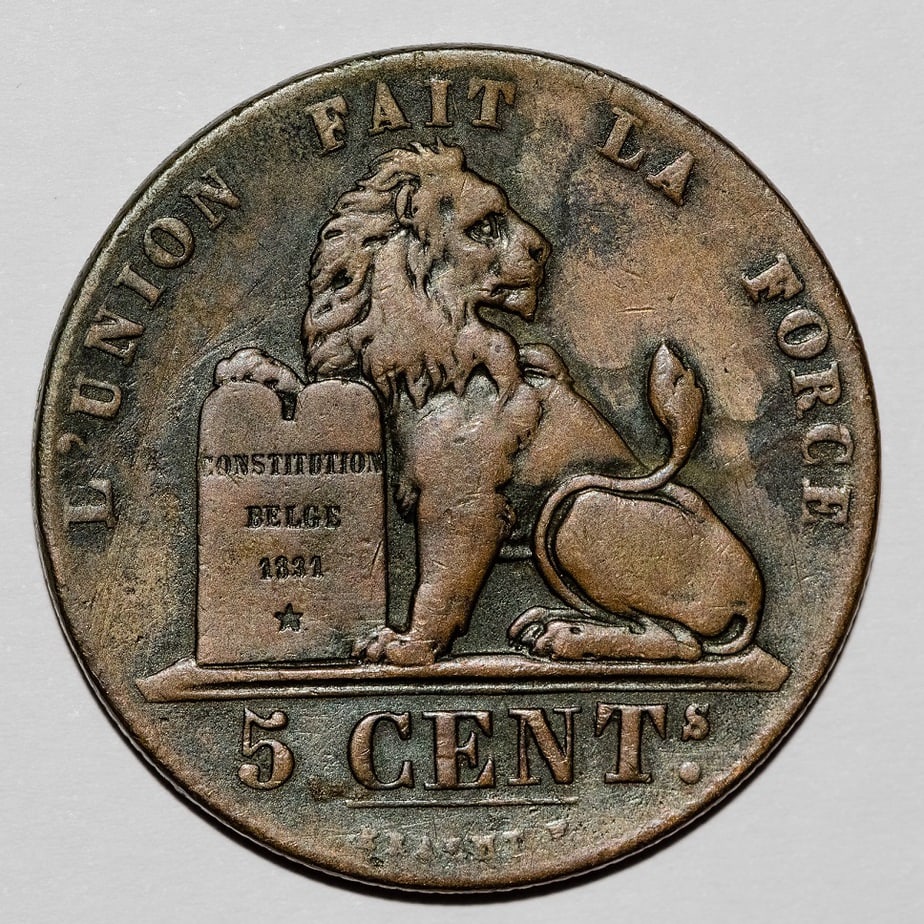

The Constitution of Belgium was approved on February 7, 1831 after the National Congress first gathered in November of the previous year to begin discussions of establishing a new government.
While the Belgian Constitution is an original document, it was inspired by the French constitutions of 1791, 1814 and 1830, the Dutch constitution of 1814, and of English constitutional law.
Since 1831, Belgium has been a parliamentary monarchy with three levels of government: the legislative, the executive, and judiciary. In addition to establishing the country’s laws and government, the Belgian Constitution provides rights and freedoms to its citizens.
Under the Constitution, all Belgians are equal before the law and no citizen can be denied his or her freedom in any way, except as ordered by a court.
Did You Know?
In order to prevent government corruption, anyone wishing to run for Belgium’s Senate, is required to pay a large amount of tax and be at least 40 years old.
5. Constitution of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Date Ratified: Sources differ; c.1814/1815
Last Amended: 1983
Author(s): Commission headed by Gijsbert Karel van Hogendorp and William I of the Netherlands
Government Type: Semi-federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy

The current version of the Dutch Constitution dates to 1983.
Like all constitutions, the Constitution of the Kingdom of the Netherlands combines the rules for the Dutch system of government and fundamental rights for the nation’s citizens.
Some of the rights outlined in the Dutch Constitution include: freedom of expression; the right to privacy; the right to vote and stand for election; and the right to equal treatment.
Did You Know?
The Constitution of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is actually only the second most important document in the country. It is subordinate to the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which regulates the constitutional relationship between the different states constituting the Kingdom (the Netherlands, Curaçao, St Maarten, and Aruba).
4. Constitution of Norway
Date Ratified: May 17, 1814
Last Amended: May 13, 2014
Author(s): Norwegian Constituent Assembly
Government Type: Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy

The Constitution of Norway or Kongeriget Norges Grundlov was adopted on May 17, 1814 and is one of the oldest existing constitutions in the world.
Similar in nature to the U.S. Constitution, the Norwegian Constitution was founded on the principals of: the sovereignty of the people; the separation of powers; and human rights.
Norway’s Constitution also establishes three different branches of government: Legislative, budgetary and supervisory power is vested in the Storting; Executive power is vested in the King and Council; and Judicial power is vested in the Supreme Courts, the subordinate courts, and the Court of Impeachment.
From the beginning, the Constitution of Norway recognized fundamental human rights that the country has strived to uphold. In fact, Norwegians are some of the happiest and most prosperous people in the world.
Did You Know?
Although the Constitution of Norway has always addressed human rights, on May 13, 2014, a series of articles on human rights were added to the Constitution.
3. Constitution of the Republic of Poland
Date Ratified: May 3, 1791
Last Amended: October 21, 2009
Author(s): Historical – Ignacy Potocki, Hugo Kołłątaj, King Stanisław August Poniatowski, Stanisław Małachowski, Stanisław Staszic, and Scipione Piattoli; Modern – Komisja Konstytucyjna and Zgromadzenia Narodowego
Government Type: Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic

Although the Constitution of San Marino is technically older, the Poland’s Constitution of 3 May 1791 is generally considered the world’s second oldest modern constitution and the oldest in Europe. (Again, the reasoning Poland’s Constitution is third on this list is that we included San Marino on this list even though parts of its constitution are uncodified.)
The 1791 Constitution set out to establish a more effective constitutional monarchy, that had a clear division of executive, legislative, and judiciary powers.
Later constitutions take inspiration from the ideas in the Constitution of 3 May 1791. Poland’s modern constitution was put into effect in 1997 and it was last amended in 2009.
Did You Know?
While Poland’s Constitution of 3 May 1791 is historically significant for the country – May 3 is a Polish national and public holiday – the constitution was only in effect for one year due to the Russo-Polish War of 1792.
2. United States Constitution
Date Ratified: June 21, 1788
Last Amended: May 5, 1992
Author(s): Constitutional Convention
Government Type: Federal presidential constitutional republic

While the Constitution of San Marino is nearly 200 years older, the United States Constitution is often considered the oldest constitution in the world because not all of San Marino’s Constitution is codified.
Additionally, the United States Constitution was the first permanent constitution of its kind and influenced the constitutions of several other countries.
The United States Constitution was ratified on June 21, 1788 after nine of the 13 original states signed.
The Constitution went into effect the following March and a new government was established. Since then, the United States Constitution has been amended 27 times, with the first ten amendments collectively known as the Bill of Rights.
Did You Know?
Many of the United States’ founding fathers did not sign the Constitution, including Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry, and John Hancock.
1. Constitution of San Marino
Date Ratified: October 8, 1600
Last Amended: 2002
Author(s): Camillo Bonelli
Government Type: Unitary parliamentary diarchic directorial republic

San Marino’s current legal system is still based on this 1600 Constitution, so it counts as the world’s oldest existing constitution.
The Constitution of San Marino or Statuta Decreta ac Ordinamenta Illustris Reipublicae ac Perpetuae Libertatis Terrae Sancti Marini, was written in Latin and contained in six books. It was last amended in 2002 when the Declaration of Citizen Rights from 1974 was updated.
Did You Know?
San Marino’s Constitution was influenced by the Corpus Juris Civilis and Roman customary law.
OTHER POSTS YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN











Second oldest constitution was polish constitution from 3rd May 1791.
Ukrainian – 1710
Actually second oldest constitution was Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth constitution.
Sorry, we are missing Switzerland. 1848!
The Constitution of 3 May 1791. Poland
Philip Orlic Constitution of 1710 in Ukraine.
#2 is POLAND
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Constitution_of_3_May_1791
Scotland’s constitution, the Declaration of Arbroath, dates from 1320.
Hi, good list but you are also missing Spain (aside from some others I’ve read in the comments) Maybe you could extend the list to the 20 oldest? Thanks!
I beleive The Constitution of 3rd May 1791, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was second in the World and a first of its kind in Europe. 3rd of May is a national holiday in both Poland and Lithuania today celebrating the historical act.