Held every year on December 10th, the Nobel Prize Awards are meant to celebrate those who make the most significant impacts on society. Named after Alfred Nobel, a Swedish inventor, it is regarded as one of the most prestigious awards in the world.
Most Nobel Prize winners are an average age of 58 when they are honored with the award, but there have certainly been several younger award winners who have challenged the age factor, becoming Nobel Laureates even before celebrating their 40th birthdays. In fact, some of the youngest Nobel Laureates have barely been eligible to vote at the time of their recognition!
Stay right here – we’re about to explore the eight youngest Nobel Prize winners in existence.
8. Frederick G. Banting
Year of birth: November 14, 1891
Year Won: 1923
Year won: Nobel Physiology, Medicine Prize for Insulin Discovery
Nationality: Canadian
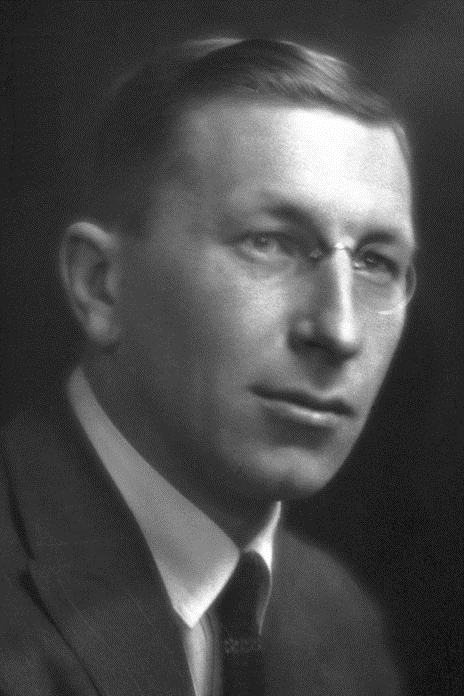

Combating challenges in the medical field is a dream come true for most scientists, and Frederick Grant Banting was no exception. Banting’s great contribution to the field of medicine was the discovery of insulin, which had a huge impact on those suffering from diabetes.
Winning the Nobel Prize alongside John Macleod, Banting still holds the record as the youngest Nobel Prize Winner in the Physiology/Medicine category at the age of 32. Other notable achievements and awards of his include the Flavelle Medal (1931) and the Cameron Prize for Therapeutics of the University of Edinburg (1927).
Did You Know?
The same year that Banting won the Nobel Prize, the Canadian government issued a lifetime annuity to continue his work.
7. Rudolf Mossbauer
Year of birth: January 31, 1929
Year Won: 1961
Year won: Nobel Physiology, Resonance Absorption of Gamma Radiation
Nationality: German

Rudolf Ludwig Mossbauer was born in Munich Germany. At the Technical University of Munich, he began his physics studies, and later came up with the Mossbauer Effect. (https://norvado.com/) His discovery saw him achieve one of the most prestigious awards in the world when he became a Nobel Prize winner in 1961.
Mossbauer’s work became popularized after Glen Rebka and Robert Pound used the Mossbauer Effect to prove the shift of gamma rays in the Earth’s gravitational field. Another of the scientist’s achievements was earning the Lomonosov Gold Medal for outstanding achievement in the natural sciences and humanities.
Did You Know?
Rudolf Mossbauer greatly influenced the German Higher Education System. He introduced departments instead of faculties permanently, influencing the position of the Technical University of Munich in German Physics.
6. Tsung-Dao Lee
Year of birth: November 24, 1926
Year Won: 1957
Year won: Nobel Prize in Physics for Investigation of Parity Laws
Nationality: Chinese-American
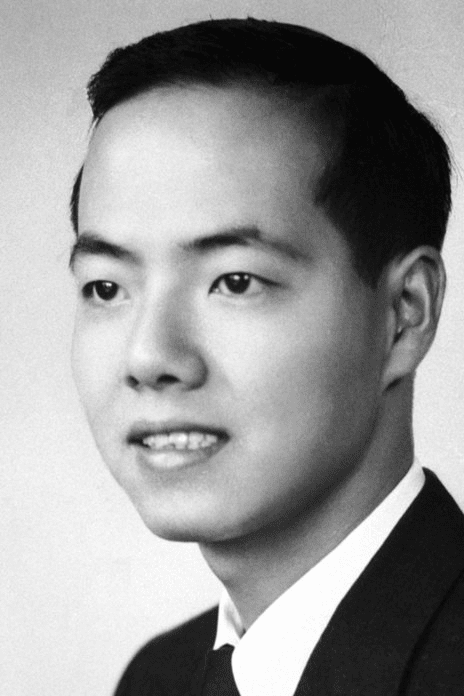
Tsung-Dao Lee was born in China, but came to embrace America as his second home in 1962. Another enthusiast of physics among our youngest Nobel winners, Lee started his science career in Chemical Engineering, but later switched to physics.
In 1957, Lee won the Nobel Prize in Physics alongside Chen Ning Yang, and the two became the first Chinese Laureates. Lee is known for Parity Laws Investigation, particle physics, and the Lee-Yang Theorem, among others.
Did You Know?
Tsung-Dao Lee is the youngest Nobel Prize Winner in American history at 31, and holds the third-youngest position of Nobel Prize winners in the Science category.
5. Carl D. Anderson
Year of birth: September 3, 1905
Year Won: 1936
Year won: Nobel Prize in Physics for the Discovery of Positron
Nationality: American

Born to Swedish immigrants, Carl David Anderson was always a determined student. He completed his undergraduate studies at 22, and obtained his Ph.D. at 25. His journey to discover positron – a subatomic particle with the same mass as an electron, but with a positive charge – began with studying cosmic rays, and the discovery went on to validate Paul Dirac’s prediction of positron’s existence.
Other than the Nobel Prize, Anderson received the Elliott Cresson Medal in 1937. He also published several different pieces throughout his life, including The Strange Case of the Cosmic Rays in 1957.
Did You Know?
During his lifetime, Anderson made another discovery of a subatomic particle, the muon, with the help of his student, Seth Neddermeyer.
4. Paul Dirac
Year of birth: August 8, 1902
Year Won: 1933
Year won: Nobel Prize in Physics, Atomic Theory Discoveries
Nationality: British

Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac was a theoretical physicist known for formulating the Dirac Equation. He is one of the early contributors to quantum mechanics and electrodynamics. Born to a Swiss father and an English mother, Dirac was brought up in Bristol in southwest England, where he earned his electrical engineering degree at the University of Bristol.
In 1932, Dirac was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge. In 1933, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. He wrote 11 papers during World War II.
Did You Know?
Despite graduating with first-class honors, Dirac couldn’t find work because of the post-war depression. With his lack of employment, he decided to further his education. It was at St. John’s College that he consequently followed his passion for general relativity theory and quantum physics.
3. Werner Karl Heisenberg
Year of birth: December 1, 1901
Year Won: 1932
Year won: Nobel Prize in Physics for Quantum Mechanics Formation
Nationality: German
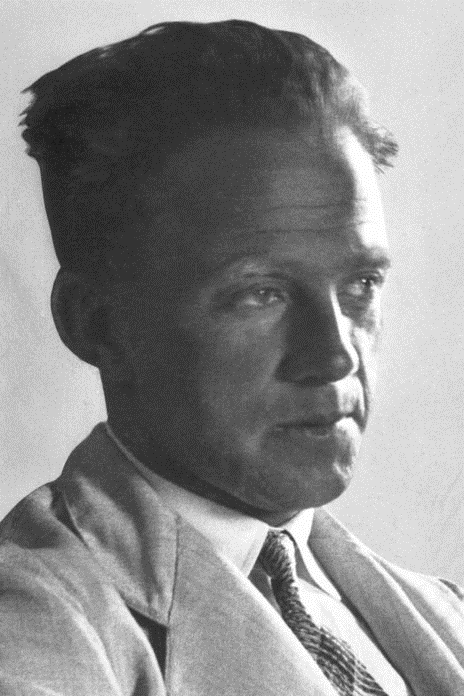

Born in Wurzburg Germany, Werner Karl Heisenberg loved to study philosophy – especially the works of Plato – and argued that mathematics formed the basis of expressing ideas. After studying physics and mathematics at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, he published his first work in a breakthrough paper in 1925. In 1932, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics.
Werner became known for the Uncertainty Principle, a work that he published in 1927. He is the recipient of many awards, such as Matteucci Medal (1929) and the Max Planck Medal (1933).
Did You Know?
Heisenberg was the only Nobel Prize winner in 1932. He was involved in creating the first West German nuclear reactor.
2. Lawrence Bragg
Year of birth: March 31, 1890
Year Won: 1915
Year won: Nobel Prize in Physics, Crystal Structure Analysis through the use of X-Rays.
Nationality: Australian-British
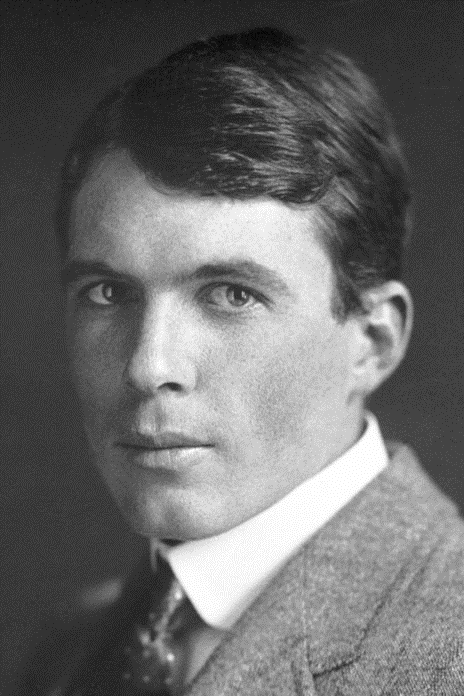

Born William Lawrence Bragg, the science and mathematical enthusiast earned myriad awards throughout his life. In a sense, his “science” career began after he broke his arm while riding a bike; this event led him to become the first recipient of his father’s experimental equipment on the surgical use of X-rays. That was the first use of such equipment in Australia.
Bragg provided technical support to the military in World War II. With the help of other colleagues, he came up with a device that helped pinpoint the location of incoming gunfire. For this, he received the Military Cross Award. Other achievements include the Royal Medal, the Hughes Medal, and the Copley Medal, among others.
Bragg jointly published several books with his father on the study of science, including the Atomic Structure of Minerals (1937). To date, he remains the youngest Nobel Science Laureate.
Did You Know?
In 1909, Bragg nailed a mathematical test while in bed suffering from pneumonia. The test would earn him a scholarship to the prestigious Trinity College, Cambridge.
1. Malala Yousafzai
Year of birth: July 12, 1997
Year Won: 2014
Year won: Nobel Prize for Fighting for Female Education, Children and Youth Oppression
Nationality: Pakistani

Malala Yousafzai is the youngest Nobel Prize Winner at 17 years of age.
Since early childhood, Yousafzai hasn’t been one to shy away from conflicts. She became a female education activist, and was nominated by Desmond Tutu for the International Children’s Peace Prize.
Born in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, northwest Pakistan (where girls couldn’t attend school), she found herself blogging for BBC Urdu about her life. She was 12 years old at the time. The New York Times made a documentary about her life, and from there, her activist efforts blew up all over the world.
Did You Know?
Yousafzai is the second Pakistani citizen to earn a Nobel Prize. She is Pakistan’s “Most Prominent Citizen” according to the former Pakistani Prime Minister. In 2012, she was shot in the head – an assassination attempt by the Taliban trying to retaliate. Luckily, she was flown to Birmingham for further medical care, and recovered.