In recent years, astronomers have discovered some of the oldest known galaxies, which formed not too long after the Big Bang — which took place about 13.8 billion years ago.
As technology has improved, scientists have been able to detect galaxies that stretch further back to the early formation of the universe.
Over the last decade, astronomers have been able to uncover galaxies that are older and further than the last galaxy to hold those titles.
What’s fascinating is that all of the galaxies on this list formed less than a billion years after the Big Bang with the oldest galaxy forming only 400 million years after the event, what’s not fascinating are their names, but please bear with us.
7. IOK-1
Age: about 12.88 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=6.96 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Lyman-alpha emitter
Year Discovered: 2006
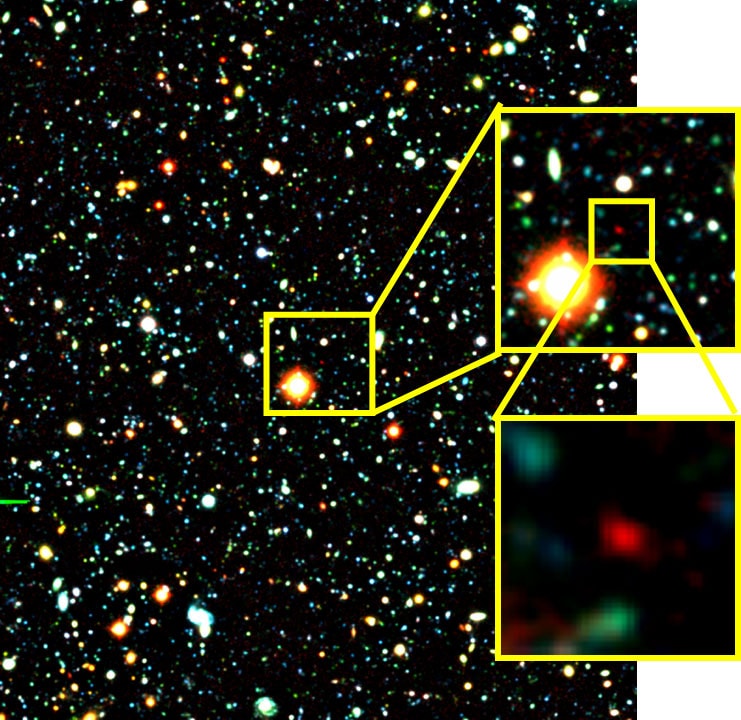 photo source: Wikimedia Commons
photo source: Wikimedia Commons
IOK-1 was discovered in 2006, a decade before GN-z11, the current oldest known galaxy, by a team of astronomers using the Subaru telescope in Hawaii. At the time, the discovery of IOK-1 was huge, as the team had looked over 60 million years further back in time than any other astronomers ever had.
The galaxy is 12.88 billion years old and formed 750 million years after the Big Bang, which occurred 13.8 billion years ago.
IOK-1 is named for scientists who discovered it — Masanori Iye of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), Kazuaki Ota of the University of Tokyo, Nobunari Kashikawa also from NAOJ.
6. GN-108036
Age: 12.9 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=7.213 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Irregular
Year Discovered: 2011
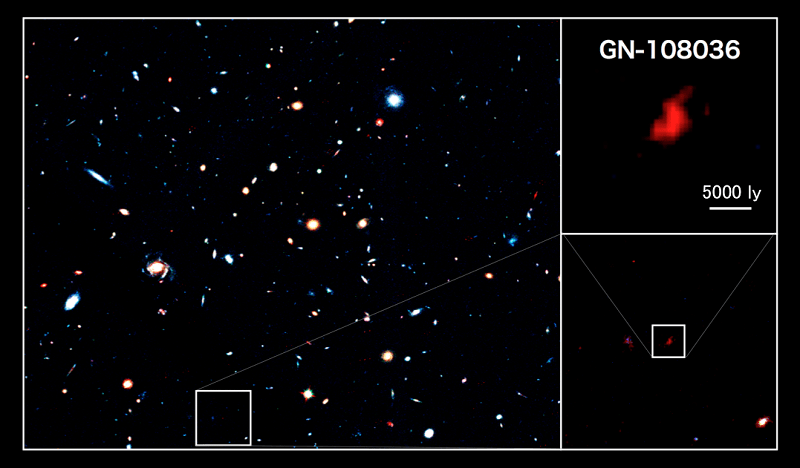 photo source: subarutelescope.org
photo source: subarutelescope.org
Galaxy GN-108036 was initially spotted by astronomers using Japans’ Subaru telescope in Hawaii in 2011. The galaxy’s distance was confirmed using by the Keck Observatory and the Hubble Space Telescope and infrared Spitzer Space Telescope were both used to take better images of the galaxy.
At the time, the discovery of the galaxy was surprising to scientists who said that they had not found galaxies as bright at GN-108036 so early in the history of the universe.
The galaxy is about 12.9 billion years old and formed around 750 million years after the Big Bang. Astronomers say that the galaxy is exceptionally bright for its size and that it has a high rate of new star formation.
5. SXDF-NB1006-2
Age: 12.91 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=7.215 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Lyman-alpha emitter
Year Discovered: 2012
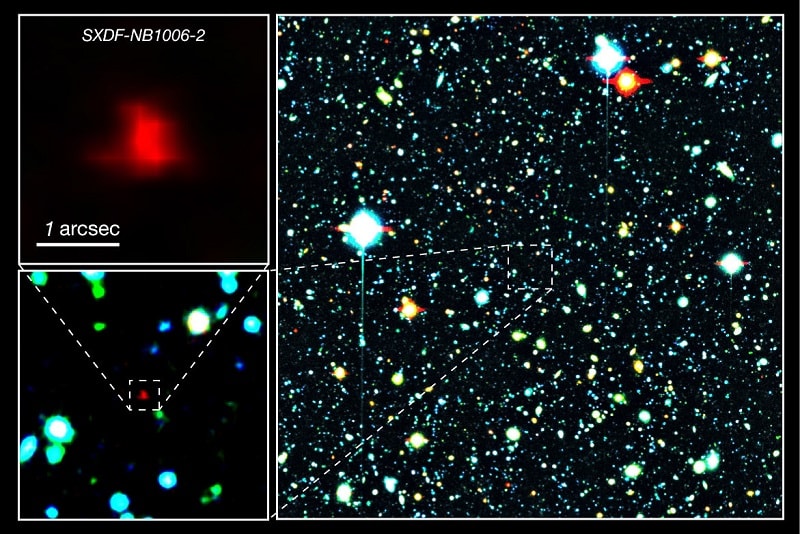 photo source: astronomynow.com
photo source: astronomynow.com
SXDF-NB1006-2, another distant galaxy from the early days of the universe, was discovered in 2012 by scientists using the Subaru and Keck telescopes. Like all the other galaxies on this list, at the time of its discovery, SXDF-NB1006-2 was the oldest known galaxy in the universe.
It is 12.91 billion years old and started to form about 800 million years after the Big Bang. In 2016, scientists discovered the presence of oxygen coming from the SXDF-NB1006-2.
The astronomers used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile to find the oxygen. The discovery of oxygen at such a great distance will help scientists piece together the early Universe.
4. z8_GND_5296
Age: 13.1 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=7.51 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Dwarf
Year Discovered: 2013
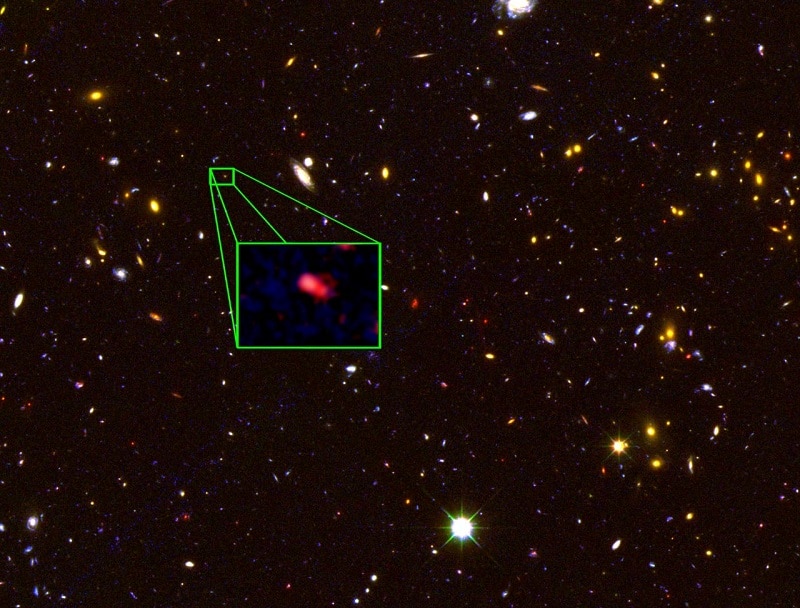 photo source: sci-news.com
photo source: sci-news.com
The galaxy, labeled z8_GND_5296, was discovered in 2013 by a team of astronomers led by Dr. Steven Willner from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. At the time, and until early 2015, the galaxy was the oldest and most distant galaxy ever discovered.
The distant galaxy was discovered using the Multi-Object Spectrometer for Infra-Red Exploration (MOSFIRE) at the W.M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii.
In 2013, MOSFIRE was new and was notable for being more sensitive than other instruments at the time and its ability to detect infrared light from multiple objects at one time.
3. EGS-zs8-1
Age: 13.13 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=7.73 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Lyman-break galaxy
Year Discovered: 2015
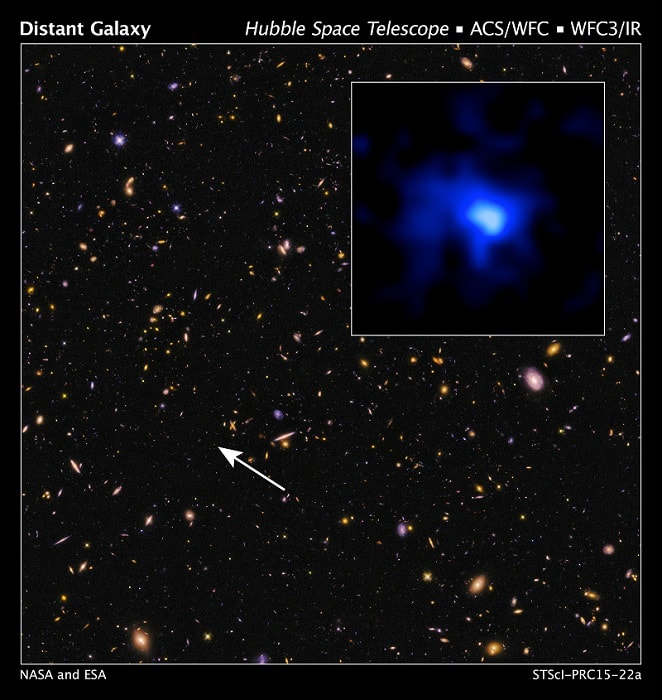 photo source: Wikipedia
photo source: Wikipedia
Galaxy EGS-zs8-1 was discovered a few months before galaxy EGSY8p7 (which is now further and older), which at the time made it the oldest galaxy in the observable universe.
The galaxy is 13.13 billion years old and was born 670 million years after the Big Bang.
In 2013, the galaxy was first spotted by astronmer Pascal Oesch while looking at Hubble Space Telescope images — Oesch was also responsible for observing several of the galaxies on this list.
Oesch confirmed his find using the Spitzer Space Telescope and announced his discovery in May 2015.
2. EGSY8p7
Age: 13.2 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=8.68 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Lyman-alpha emitter
Year Discovered: 2015
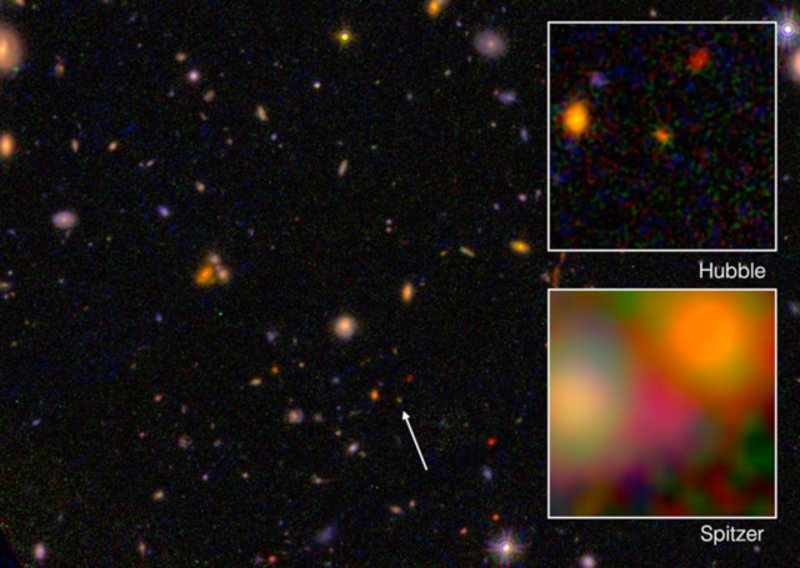 photo source: Wikipedia
photo source: Wikipedia
Until the discovery of galaxy GN-z11 in 2016, galaxy EGSY8p7 (also designated as (EGSY-2008532660) was the oldest and most distant known object in the universe. In 2015, it was determined that the galaxy was 13.2 billion years old and formed about 570 million years after the Big Bang.
Pascal Oesch, one of the people who discovered the galaxy, used the W.M. Keck Observatory to find EGSY8p7.
One of the most notable characteristics of the galaxy is that it is the most distant known detection of hydrogen’s Lyman-alpha emissions. According to researchers, these emissions should have been absorbed by neutral hydrogen (atomic hydrogen) clouds filling the early universe.
1. GN-z11
Age: 13.4 billion years old
Distance from Earth: z=11.09 (z = redshift)
Galaxy Type: Irregular
Year Discovered: 2016
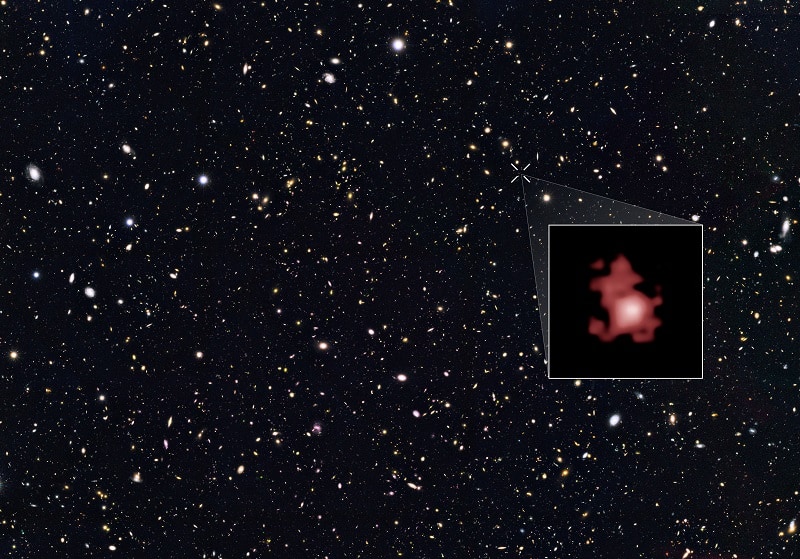 photo source: Wikipedia
photo source: Wikipedia
As of 2016, galaxy GN-z11 is the oldest and most distant galaxy in the known universe. GN-z11 has an estimated age of 13.4 billion years.
The galaxy was discovered by a team studying data from the Hubble Space Telescope’s Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey (CANDELS) and Spitzer Space Telescope’s Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey-North (GOODS-North).
The team released its findings in March 2016 and revealed that the galaxy was much older than researchers originally thought as it is located at the distance limit of the what the Hubble Telescope can observe.
The discovery of the galaxy is important because it provides new insight into the early formation of the universe.
OTHER POSTS YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN