Although its often the first school program to be cut and is generally undervalued by the majority of the population, art is one of the most important aspects of human culture. Long before any evidence of language emerged, some of the oldest artifacts that shed light on human history have been works of art. The world’s oldest art is tens of thousands, even hundreds of thousands in some cases, years old.
These works of art show how our culture has evolved over the millennia and range from abstract lines and dots to more complex human and animal figurines. New discoveries are being made every year, so these are the oldest known pieces of art that have been uncovered so far.
10. Venus of Hohle Fels
Year Created: c.35,000 to 40,000 years ago
Location: Hohle Fels, Schelklingen, Germany
Type of Art: Venus (female) figurine
Materials Used: Carved mammoth ivory
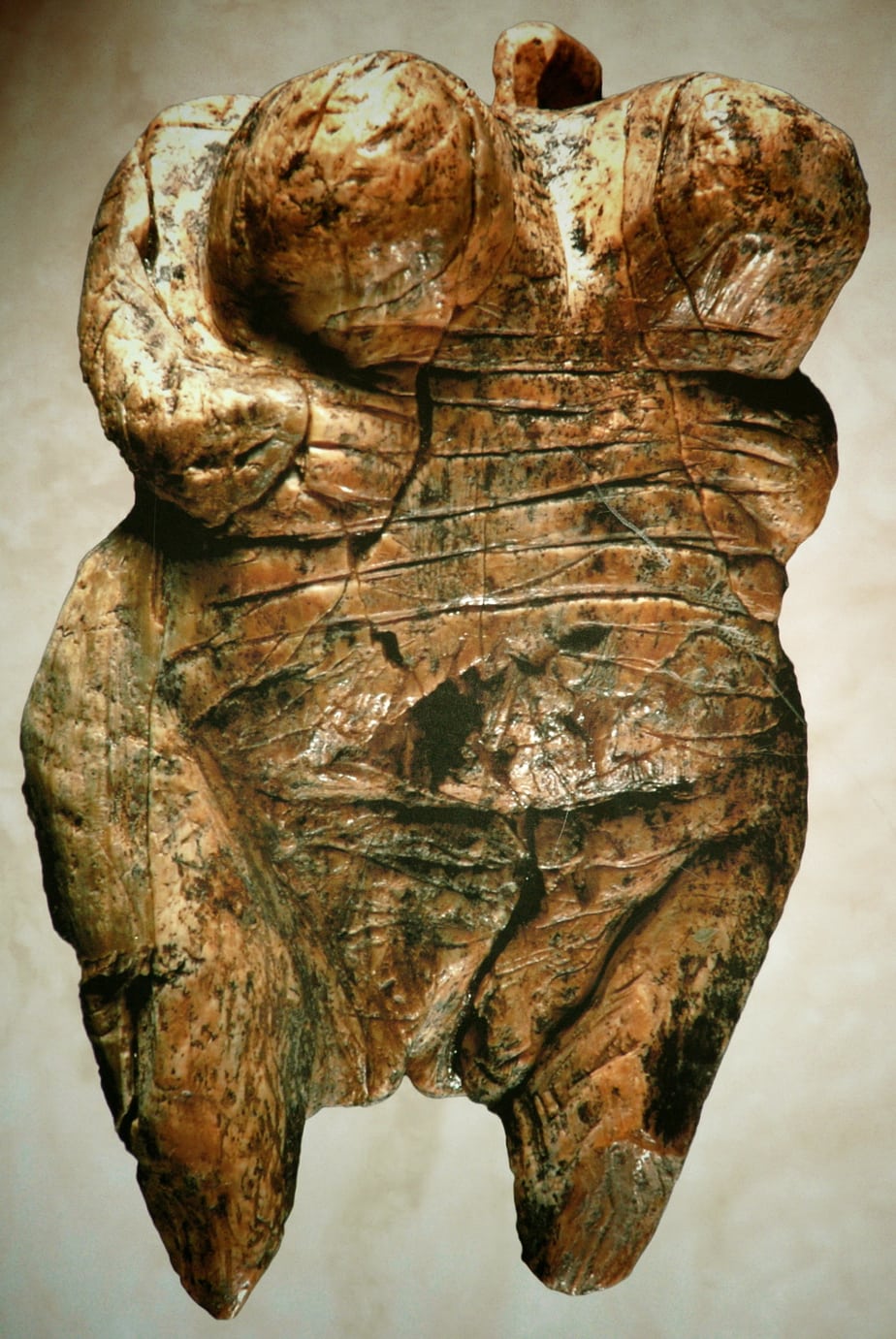

The Venus of Hohle Fels is the most famous Venus figurine ever discovered and it is the oldest undisputed depiction of a human being – there are a few other “Venuses” on this list, but they are controversial. The Hohle Fels Venus was found over a decade ago in Germany and has been dated to between 35,000 to 40,000 BCE.
The Venus of Hohle Fels is a very small figure carved out of mammoth ivory. It is less than 2.5 inches (60 millimeters) long. While the figure very clearly depicts a voluptuous women (the figure has large breasts and a womanly shape), there is no head. Instead, there is a ring where the head should be and archaeologists believe this means the figure was worn as a necklace.
Did You Know?
Due to the way the Venus of Hohle Fels was carved, scientists believe the figure may have represented female fertility, or been related to shamanistic rituals and beliefs.
9. Lion Man of the Hohlenstein Stadel
Year Created: c.38,000 to 40,000 BCE
Location: Hohlenstein-Stadel, Swabian Jura, Germany
Type of Art: Lion-man figurine
Materials Used: Carved piece of mammoth ivory using a flint stone knife
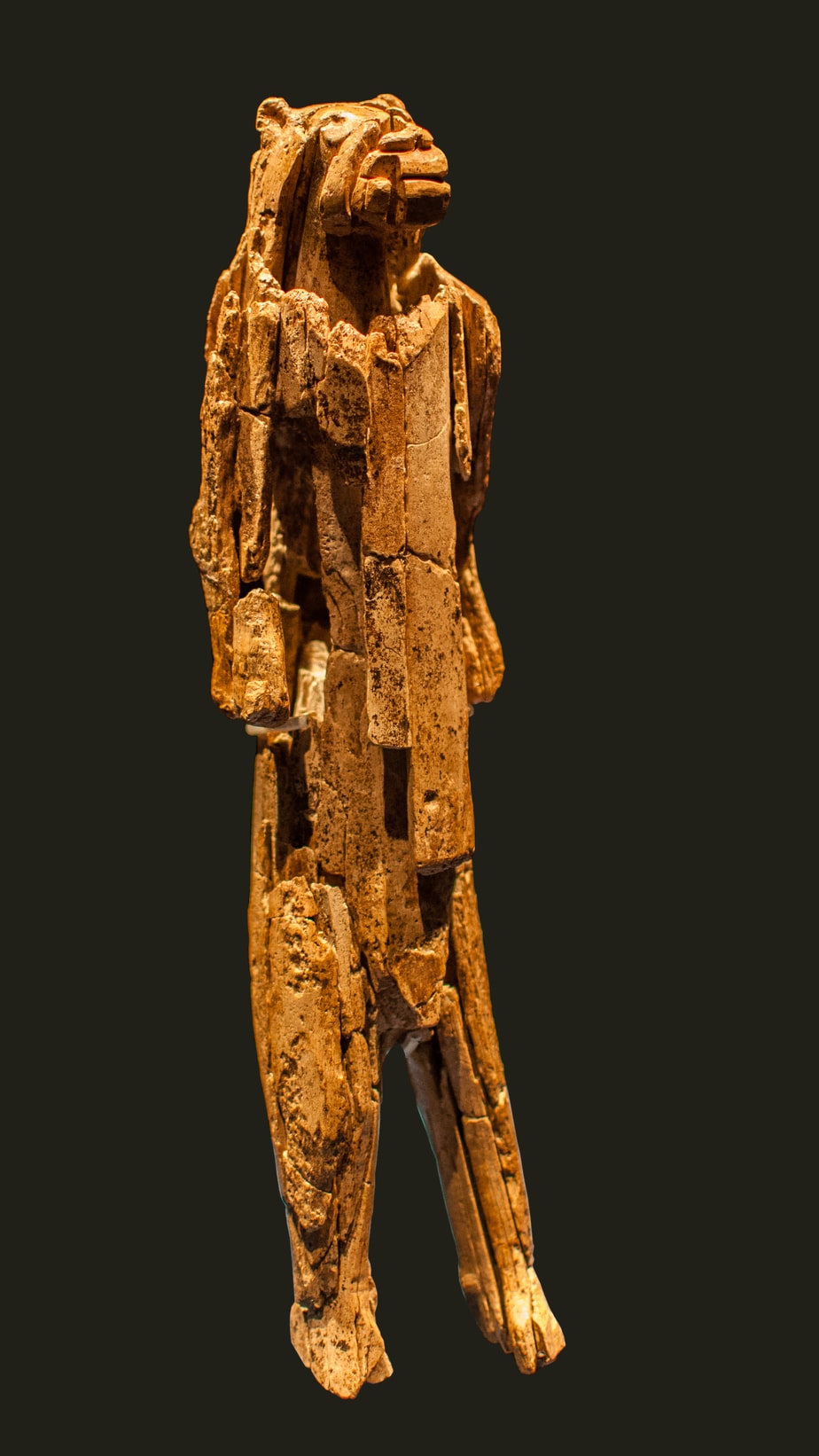

The Lion Man of Hohlenstein Stadel or Löwenmensch (“lion-human”) is one of the most fascinating pieces of prehistoric art ever discovered. As the figurine’s name suggests, the Lion Man depicts a lion’s head on a man’s body. The Löwenmensch was carved from a piece of mammoth ivory and is widely considered the oldest uncontested example of figurative art. It is also the oldest known zoomorphic (animal-shaped) sculpture in the world.
While most of the Lion Man sculpture was uncovered in 1939, more pieces were discovered in 2009. A few years later, from 2012 to 2013, the Lion Man was carefully reconstructed and these new pieces were added. Currently, the Lion Man is on display at the Ulm Museum in Germany.
Did You Know?
In more recent years, the gender of the Lion Man has been called into question. Some scientists have argued that the lion head of the figure is actually a ”Höhlenlöwin” (female European cave lion).
8. Borneo Cave Art
Year Created: c.40,000 years ago
Location: Borneo (Kalimantan), Indonesia
Type of Art: Wild cattle drawing
Materials Used: Ochre on cave walls
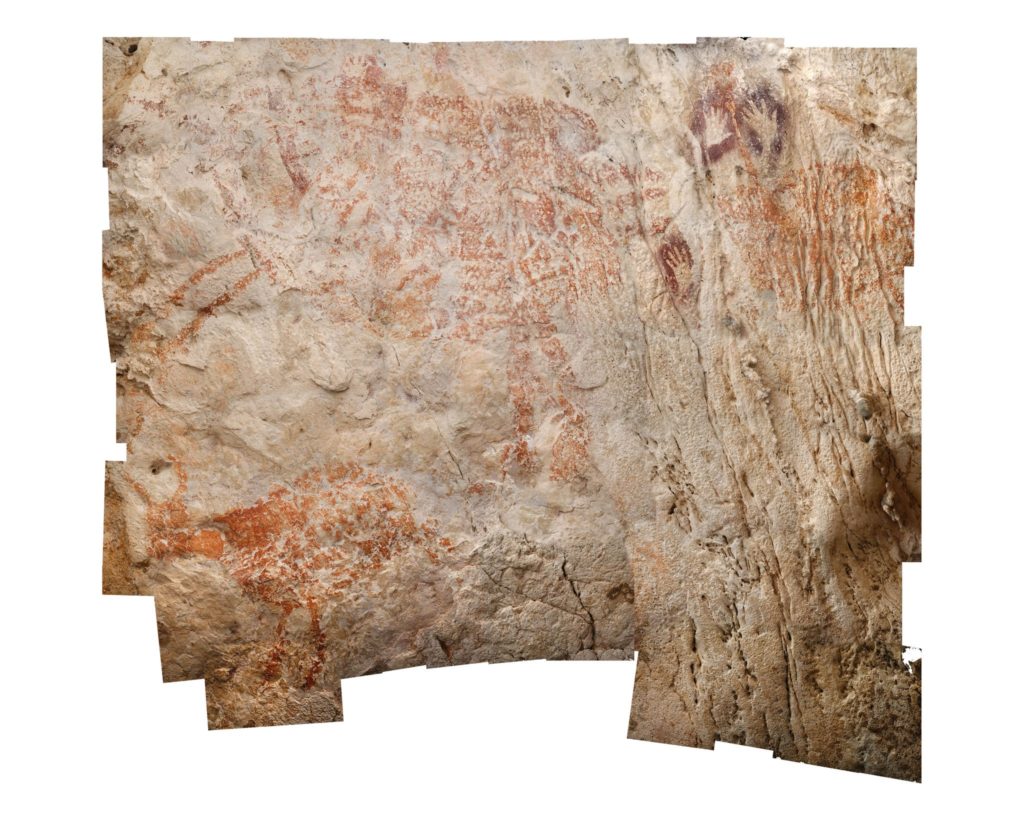

Recently, in late 2018, archaeologists discovered what is now the world’s oldest figurative art in a cave in Borneo, Indonesia. The cave art shows pictures of wild cattle made with red ochre and it has been dated to over 40,000 years ago, possibly up to 52,000 years ago. While many of the other art on this list is older, the images/engravings depicted are abstract lines and drawings and do not necessarily represent anything the way these cattle drawings do.
Like many newer archaeological finds, the cave art in Borneo was dated using a newer technique, flowstone dating, rather than radiocarbon dating. According to archaeologists, the date of the Borneo cave art shows that humans were shifting from abstract to more figurative art around the same time in both Asia and Europe.
Did You Know?
The cattle drawings were not the only works of art found in the Borneo cave. There are more recent paintings of human figures and hand stencils dating between 13,000 to 20,000 years ago.
7. La Ferrassie Cave Cupules
Year Created: c. 40,000 to 60,000 BCE
Location: Les Eyzies, Dordogne, France
Type of Art: Cupules (cup shaped depressions carved into rock surface)
Materials Used: Hammerstones used to carve out cup shapes on rocks
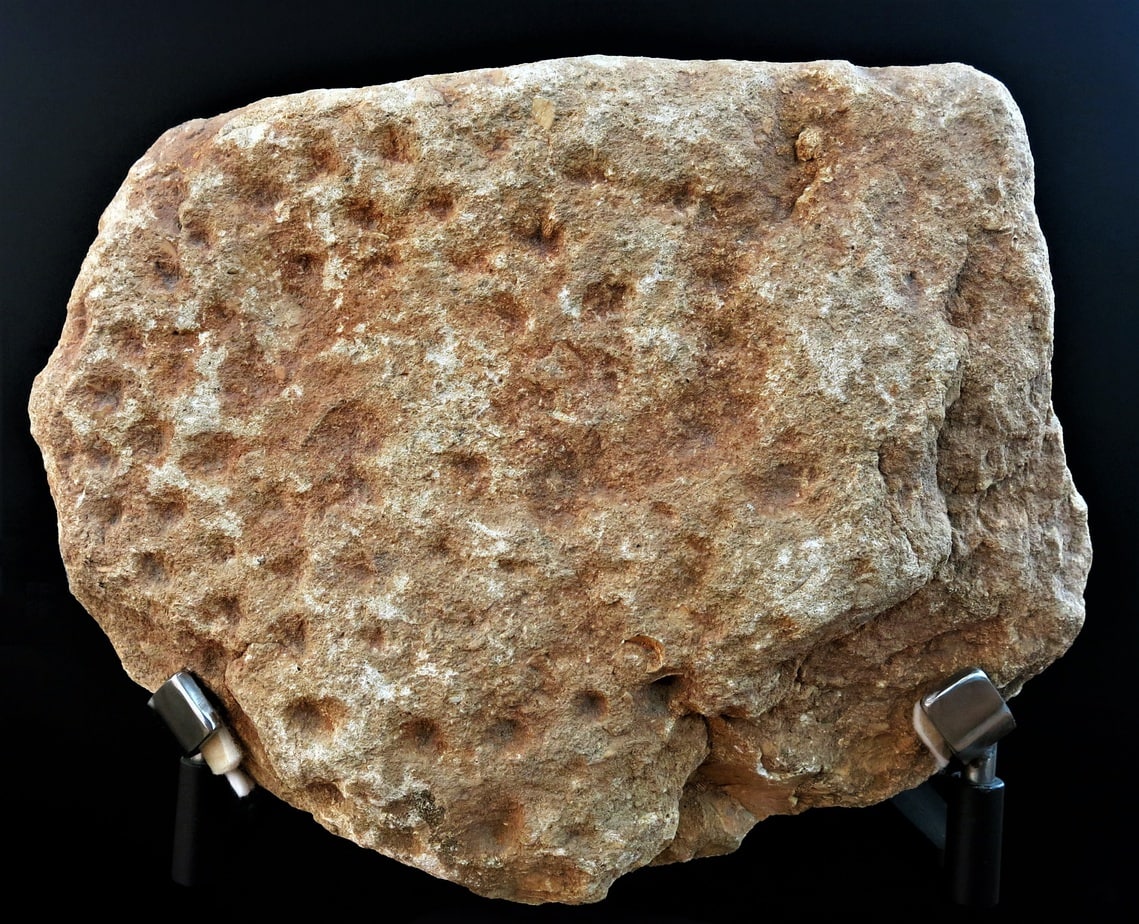

The La Ferrassie Cave complex is one of the oldest archaeological sites in France and is home to one of the oldest known art forms, cave cupules. These cup shaped depressions may not be as pretty as some of the other cave art out there, but they are just as important for shedding light on the early cultural practices of early humans.
The cupules at La Ferrassie have been dated between 40,000 to 60,000 BCE. Unfortunately, because cupules are not as “nice” as cave murals and paintings, little research has been done on the why they may have been made and how important these symbols may have been to ancient humans – cupules have been found on every continent.
Did You Know?
Although they are not as old as the cupules, La Ferrassie Cave has numerous paintings, animal figurines, and rock engravings, the most fascinating of which is believed to be a depiction of a vulva.
6. Diepkloof Eggshell Engravings
Year Created: c.60,000 BCE
Location: Diepkloof Rock Shelter, Western Cape South Africa
Type of Art: Eggshell engravings
Materials Used: Ostrich eggshells
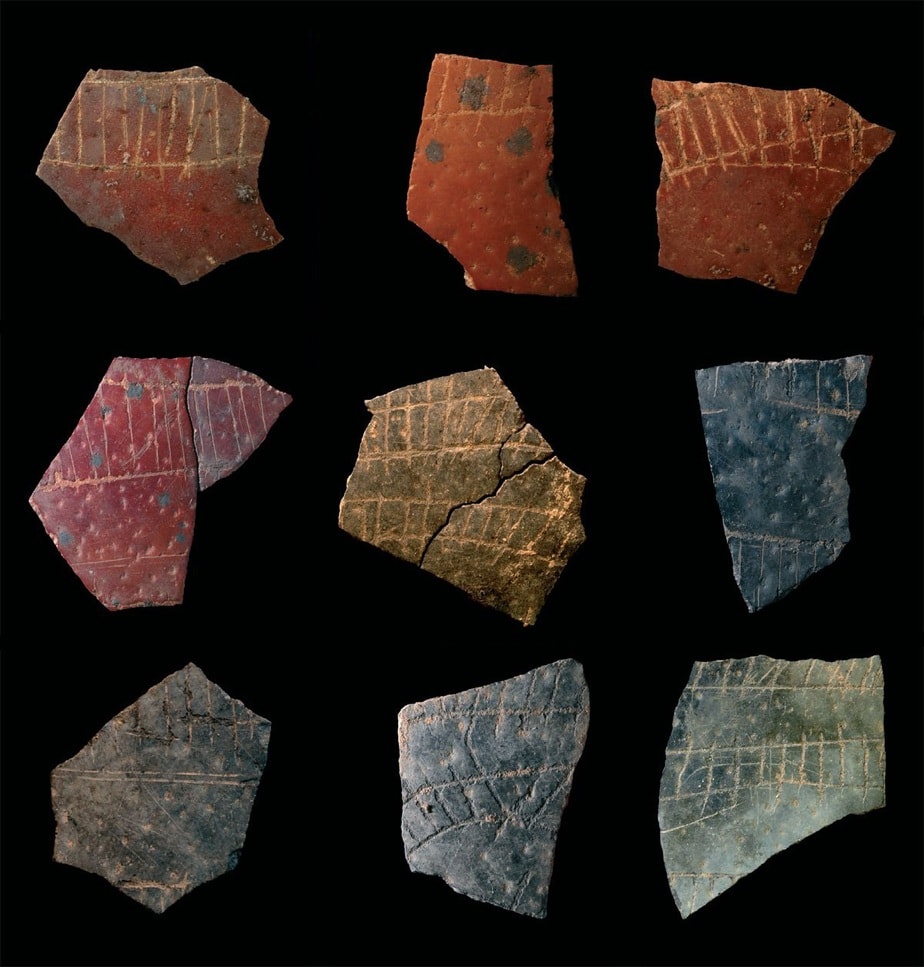

About a decade ago, in early 2010, scientists revealed that they had uncovered ancient ostrich eggshell fragments covered in etched symbols at the Diepkloof Rock Shelter in South Africa. The eggshell engravings were dated to about 60,000 BCE and have been called abstract graphic designs.
Archaeologists found that the engravings had changed over time and two main patterns emerged. The older design shows a hatched band similar to a train track, while the newer engravings consist of parallel lines. Researchers also noted that the different colors of the eggshell fragments were mostly caused by the shells being accidentally dropped into a fire and broken.
Did You Know?
There is some evidence that the Diepkloof eggshells had punctured openings, which means the empty eggs were probably used as containers.
5. Cave of Maltravieso
Year Created: 64,000 to 66,700 years old
Location: Cáceres, Extremadura, Spain
Type of Art: Hand stencils on cave walls
Materials Used: Red ochre
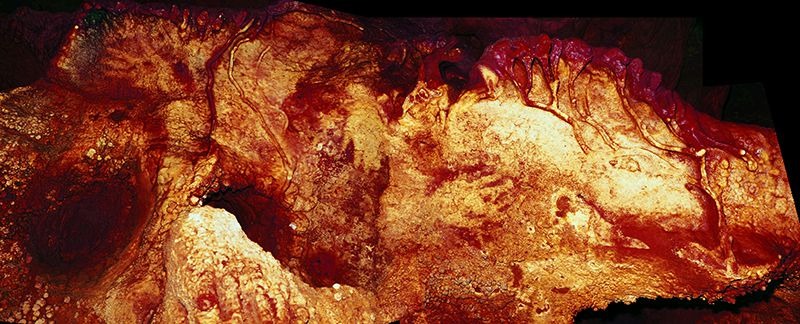
The hand stencils in the Cave of Maltravieso in Spain have changed scientists’ understandings on history of human art. The paintings in Maltravieso are so old – between 64,000 to 66,7000 years old – that they could not have been made by Homo sapiens. Instead, researchers believe that the hand stencils were made by Neanderthals (although there is no direct evidence other than the time period to suggest this).
Maltravieso’s hand stencils are currently the oldest known cave paintings in the world and were made using a red ochre pigment. The pigments were dated using a newer method called uranium-thorium dating, which is more accurate than the better-known radiocarbon dating.
Did You Know?
Two other caves in Spain – La Pasiega and Ardales – also have cave paintings made with the same red ochre used in the Cave of Maltravieso and have also been dated to over 60,000 years ago.
4. Blombos Cave Rock Art
Year Created: c.70,000 to 75,000 BCE
Location: Blombos Private Nature Reserve, Heidelberg, Western Cape, South Africa
Type of Art: Rock engravings
Materials Used: Ochre crayons on cave rock
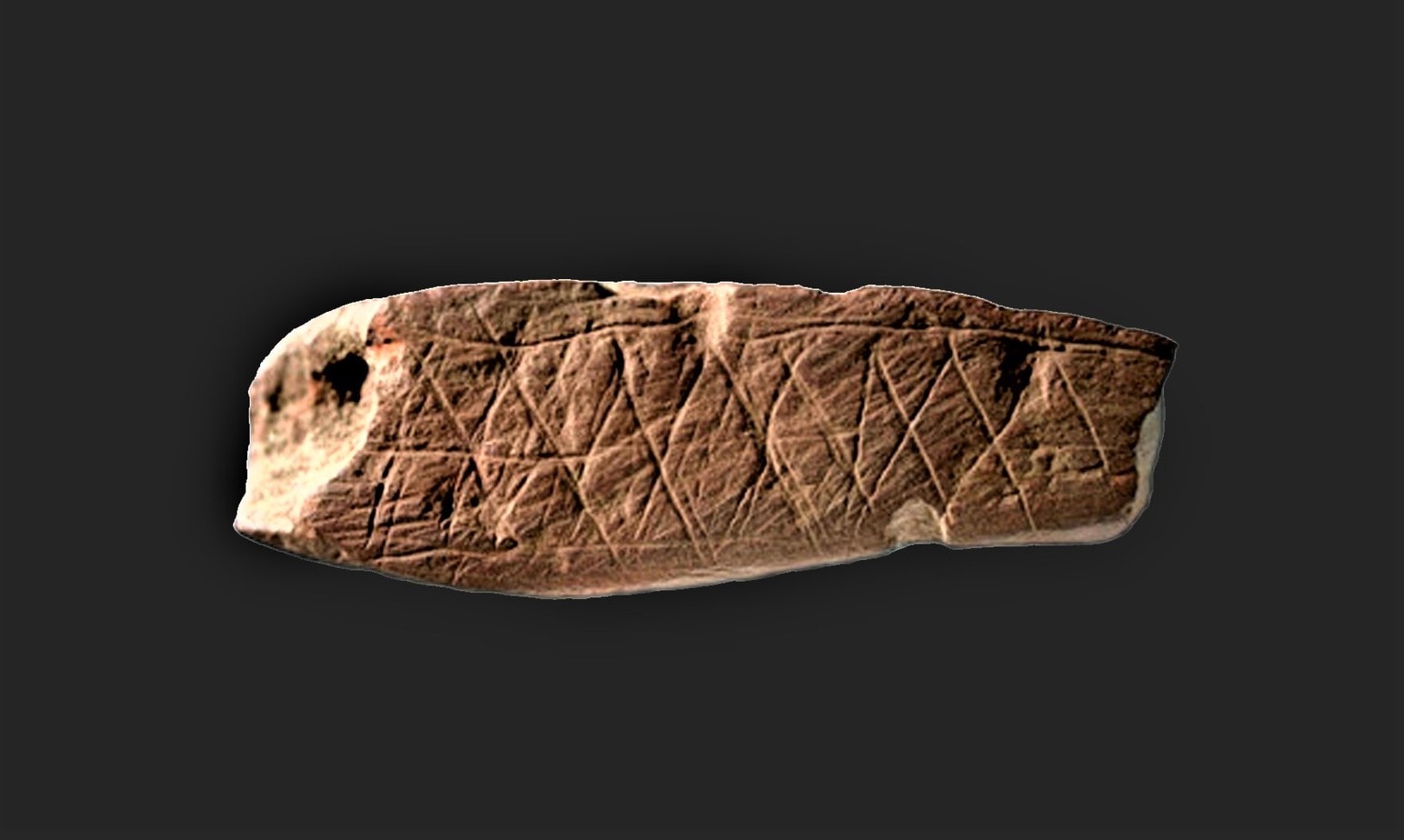

The Blombos Cave in South Africa is a treasure trove of prehistoric art which dates back to at least 70,000 BCE. The art of Blombos Cave is the earliest known art ever discovered in Africa and pre-dates other early cave art by tens of thousands of years.
The most important discovery in the Blombos Cave was two pieces or rocks decorated with crosshatch designs that were made with ochre crayons. Archaeologists discovered hundreds of piles of ochre that had been ground up and turned into these crayons. While scientists believe that these crayons were made specifically for design purposes, no actual cave art/paintings have been discovered yet in Blombos.
Did You Know?
Besides the rock carvings, shell beads dating to around 70,000 to 75,000 BCE were found in Blombos Cave.
3. Venus of Tan-Tan
Year Created: c.200,000 to 500,00 BCE
Location: Tan-Tan, Morocco
Type of Art: Venus (female) figurine
Materials Used: Quartzite rock
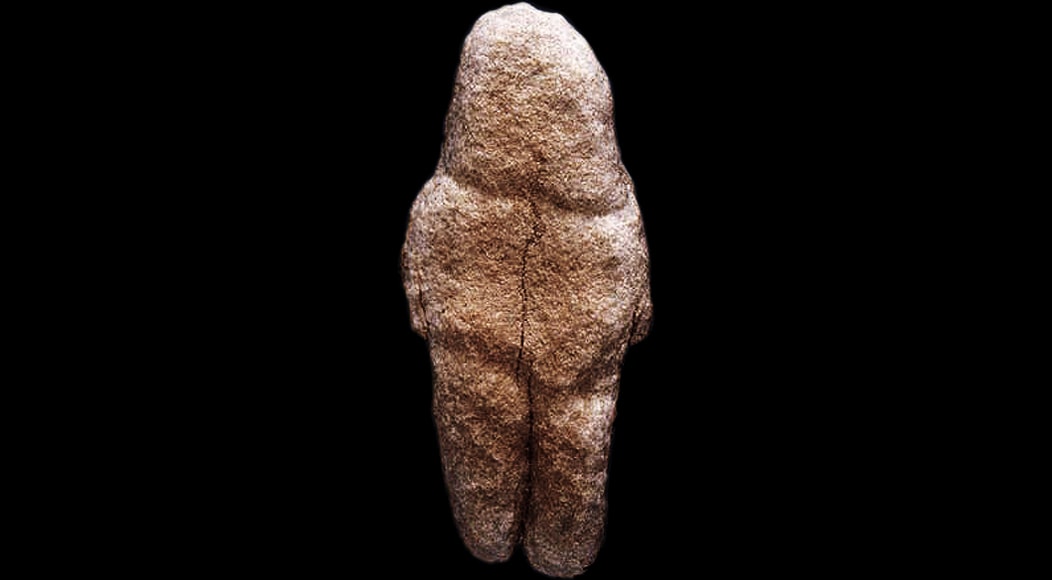

Like the Venus of Berekhat Ram, which dates to around the same time period, the Venus of Tan-Tan’s status as a piece of art has been called into question. The Venus of Tan-Tan and the Venus of Berekhat Ram are often mentioned together because their existence and dating to over 200,000 BCE provides evidence that these figures may have been made by early human ancestors and not just natural phenomena.
The Venus of Tan-Tan has been studied extensively and scientists do agree that some of the markings on the rock were natural. However these researchers believe that the natural lines of the Venus of Tan-Tan were accentuated by human tools.
Did You Know?
The Venus of Tan-Tan is made out of quartzite rock and is 6 centimeters in length (2.36 inches), roughly 2.6 centimeters (1.02 inches) in width, and 1.2 centimeters (0.47 inches) thick.
2. Venus of Berekhat Ram
Year Created: c.230,000 to 700,000 BCE
Location: Berekhat Ram, Golan Heights, between Syria and Israel
Type of Art: Venus (female) figurine
Materials Used: Carved red tuff pebble (rock made from volcanic ash)
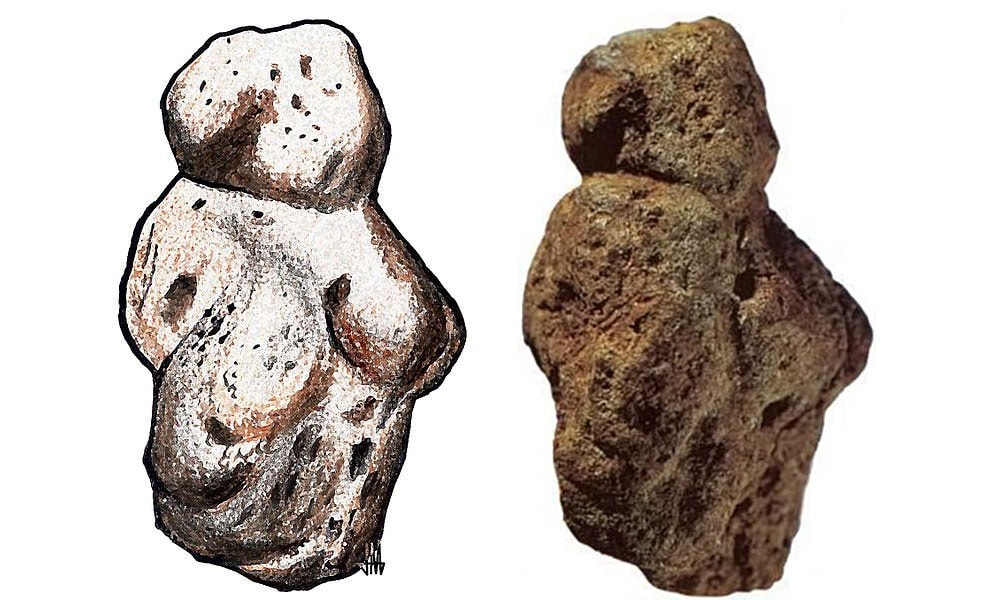

The Venus of Berekhat Ram is a controversial piece of art because scientists cannot agree on whether of not the red tuff pebble (volcanic ash rock) was actually carved by a person of it was shaped naturally. The figurine is being included on this list because there is a strong case for it being a real piece of art and the Venus of Berekhat Ram is mentioned often enough in discussions of prehistoric art that it deserves to be included.
While the official status of the Venus of Berekhat Ram has yet to be determined, microscopic analysis has shown that the marks on the rock were made by a sharp-edged tool. However, there are people in the scientific community who believe that marks were caused by erosion. In addition to the microscopic analysis, the Venus of Berekhat Ram has been dated to 230,000 to 700,000 BCE, which would make it one of the oldest prehistoric sculptures.
Did You Know?
The Venus of Berekhat Ram was discovered in 1981 and was named after the more famous Venus figurines from Europe even though it does not look anything like these figures.
1. Bhimbetka Petroglyphs
Year Created: c. 290,000 BCE to 700,000 BCE
Location: Raisen District, Madhya Pradesh, India
Type of Art: Cupules (cup shaped depressions carved into rock surface)
Materials Used: Hammerstones used to carve out cup shapes on rocks
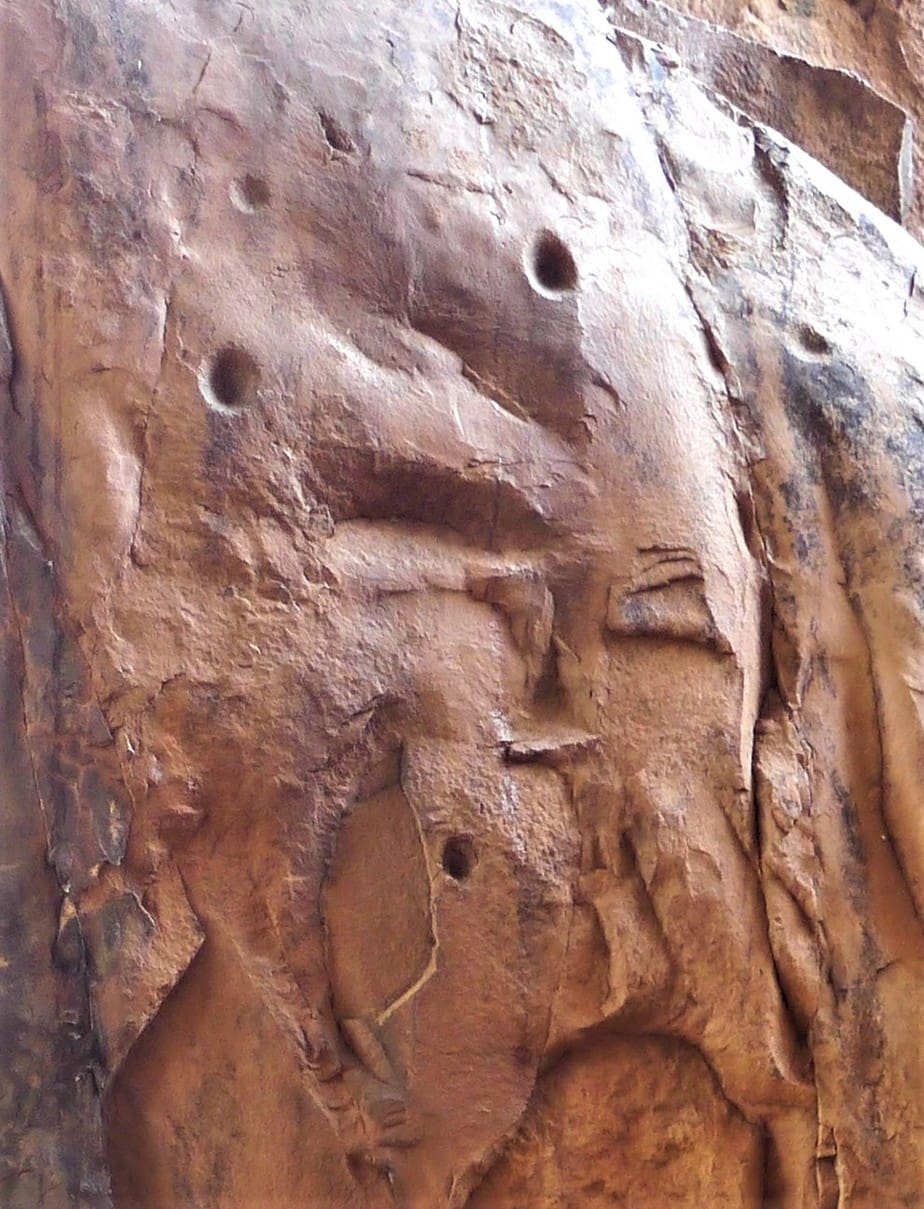

The petroglyphs or rock carvings at the Bhimbetka rock shelter in Madhya Pradesh, India have been dated to at least 290,000 BCE – there is speculation that the carvings could be thousands of years older, but further testing is needed. The rock carvings primarily consist of cupules (cup shaped depressions that have been hammered into the rock surfaces) and are the world’s oldest known art.
While the Bhimbetka cave complex is made of over 700 rock shelters, the most famous part of the site is the Auditorium Cave. It is the largest of the Bhimbetka shelters and is surrounded by quartzite rock towers which can be seen from over several kilometers away.
Did You Know?
In addition to the petroglyphs, the Bhimbetka rock shelters are home to over 500 cave murals and other examples of paleolithic art. These paintings are not nearly as old as the petroglyphs and are only about 30,000 years old.